Probléma: A 2 I és J folyamatnak köszönhetően olyan programot kell írnia, amely garantálhatja a kettő közötti kölcsönös kizárást további hardver -támogatás nélkül.
A CPU óraciklusok pazarlása
Laikus szempontból, amikor egy szál várta a sorát, egy hosszú ideig tartó hurok alatt véget ért, amely másodpercenként milliószor tesztelte a feltételt, így szükségtelen számítással. Van egy jobb várakozási mód, és az néven ismert 'hozam' -
Annak megértése érdekében, hogy mit tesz, mélyen mélyítenünk kell a folyamat ütemező működését a Linuxban. Az itt említett ötlet az ütemező egyszerűsített verziója, amelyben a tényleges megvalósítás rengeteg komplikációval rendelkezik.
Vegye figyelembe a következő példát
Három folyamat van a P1 P2 és P3 folyamat. A P3 folyamat olyan, hogy a kódunkhoz hasonló hurok, amely nem olyan hasznos számítással rendelkezik, és a hurokból csak akkor létezik, amikor a P2 befejezi annak végrehajtását. Az ütemező mindet egy kerek Robin sorba helyezi. Tegyük fel most, hogy a processzor órasebessége 1000000/sec, és minden egyes iteráció során 100 órát oszt ki. Ezután az első P1 -et 100 órára (0,0001 másodperc) futtatják, majd a P2 (0,0001 másodperc), majd a P3 (0,0001 másodperc), mivel nincs több folyamat, ez a ciklus megismétlődik, amíg a P2 véget nem ér, majd a P3 végrehajtása és végül annak befejezése.
Ez a 100 CPU óraciklus teljes pazarlása. Ennek elkerülése érdekében kölcsönösen feladjuk a CPU időszeletét, azaz a hozamot, amely lényegében ezúttal véget ér ezúttal, és az ütemező felveszi a következő futási folyamatot. Most egyszer teszteljük állapotunkat, akkor feladjuk a CPU -t. Tekintettel arra, hogy a tesztünk 25 órás ciklust vesz igénybe, számításunk 75% -át megtakarítjuk egy időben szeletben. Hogy ezt grafikusan tegyem
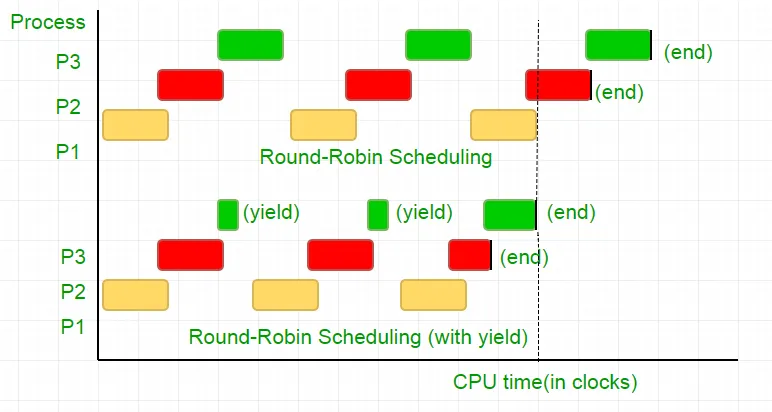
Ha a processzor órasebességét 1MHz -nek tekintjük, ez sok megtakarítás!.
A különböző eloszlások eltérő funkciókat biztosítanak ennek a funkciónak a megvalósításához. Linux biztosítja Sched_yield () -
void lock(int self) { flag[self] = 1; turn = 1-self; while (flag[1-self] == 1 && turn == 1-self) // Only change is the addition of // sched_yield() call sched_yield(); }
Memóriakerítés.
Lehet, hogy a korábbi oktatóanyag kódja a legtöbb rendszeren működött, de nem volt 100% -ban helyes. A logika tökéletes volt, de a legmodernebb CPU-k teljesítmény-optimalizálást alkalmaznak, amely a rendelésen kívüli végrehajtást eredményezheti. A memóriaműveletek (terhelések és üzletek) ezen átrendezése általában észrevétlenül marad a végrehajtás egyetlen szálán belül, de kiszámíthatatlan viselkedést okozhat az egyidejű programokban.
Vegye figyelembe ezt a példát
while (f == 0); // Memory fence required here print x;
A fenti példában a fordító a 2 állást egymástól függetlennek tekinti, és így megpróbálja növelni a kód hatékonyságát azáltal, hogy újratelepítik azokat, ami problémákat okozhat az egyidejű programok számára. Ennek elkerülése érdekében memóriakerítést helyezünk el, hogy utaljunk a fordítónak az akadályok közötti állítások közötti lehetséges kapcsolatról.
Tehát a nyilatkozatok sorrendje
zászló [self] = 1;
fordulás = 1-én;
Míg (forduljon a feltételek ellenőrzéséhez)
hozam();
Pontosan ugyanaznak kell lennie, hogy a zár működjön, különben holtpont állapotba kerül.
Annak biztosítása érdekében, hogy ez a fordítók olyan utasítást nyújtsanak be, amely megakadályozza a nyilatkozatok megrendelését ezen a gáton. GCC esetén az __sync_synchronize () -
Tehát a módosított kód lesz
Teljes megvalósítás C -ben:
// Filename: peterson_yieldlock_memoryfence.cpp // Use below command to compile: // g++ -pthread peterson_yieldlock_memoryfence.cpp -o peterson_yieldlock_memoryfence #include
// Filename: peterson_yieldlock_memoryfence.c // Use below command to compile: // gcc -pthread peterson_yieldlock_memoryfence.c -o peterson_yieldlock_memoryfence #include
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger; public class PetersonYieldLockMemoryFence { static AtomicInteger[] flag = new AtomicInteger[2]; static AtomicInteger turn = new AtomicInteger(); static final int MAX = 1000000000; static int ans = 0; static void lockInit() { flag[0] = new AtomicInteger(); flag[1] = new AtomicInteger(); flag[0].set(0); flag[1].set(0); turn.set(0); } static void lock(int self) { flag[self].set(1); turn.set(1 - self); // Memory fence to prevent the reordering of instructions beyond this barrier. // In Java volatile variables provide this guarantee implicitly. // No direct equivalent to atomic_thread_fence is needed. while (flag[1 - self].get() == 1 && turn.get() == 1 - self) Thread.yield(); } static void unlock(int self) { flag[self].set(0); } static void func(int s) { int i = 0; int self = s; System.out.println('Thread Entered: ' + self); lock(self); // Critical section (Only one thread can enter here at a time) for (i = 0; i < MAX; i++) ans++; unlock(self); } public static void main(String[] args) { // Initialize the lock lockInit(); // Create two threads (both run func) Thread t1 = new Thread(() -> func(0)); Thread t2 = new Thread(() -> func(1)); // Start the threads t1.start(); t2.start(); try { // Wait for the threads to end. t1.join(); t2.join(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println('Actual Count: ' + ans + ' | Expected Count: ' + MAX * 2); } }
import threading flag = [0 0] turn = 0 MAX = 10**9 ans = 0 def lock_init(): # This function initializes the lock by resetting the flags and turn. global flag turn flag = [0 0] turn = 0 def lock(self): # This function is executed before entering the critical section. It sets the flag for the current thread and gives the turn to the other thread. global flag turn flag[self] = 1 turn = 1 - self while flag[1-self] == 1 and turn == 1-self: pass def unlock(self): # This function is executed after leaving the critical section. It resets the flag for the current thread. global flag flag[self] = 0 def func(s): # This function is executed by each thread. It locks the critical section increments the shared variable and then unlocks the critical section. global ans self = s print(f'Thread Entered: {self}') lock(self) for _ in range(MAX): ans += 1 unlock(self) def main(): # This is the main function where the threads are created and started. lock_init() t1 = threading.Thread(target=func args=(0)) t2 = threading.Thread(target=func args=(1)) t1.start() t2.start() t1.join() t2.join() print(f'Actual Count: {ans} | Expected Count: {MAX*2}') if __name__ == '__main__': main()
class PetersonYieldLockMemoryFence { static flag = [0 0]; static turn = 0; static MAX = 1000000000; static ans = 0; // Function to acquire the lock static async lock(self) { PetersonYieldLockMemoryFence.flag[self] = 1; PetersonYieldLockMemoryFence.turn = 1 - self; // Asynchronous loop with a small delay to yield while (PetersonYieldLockMemoryFence.flag[1 - self] == 1 && PetersonYieldLockMemoryFence.turn == 1 - self) { await new Promise(resolve => setTimeout(resolve 0)); } } // Function to release the lock static unlock(self) { PetersonYieldLockMemoryFence.flag[self] = 0; } // Function representing the critical section static func(s) { let i = 0; let self = s; console.log('Thread Entered: ' + self); // Lock the critical section PetersonYieldLockMemoryFence.lock(self).then(() => { // Critical section (Only one thread can enter here at a time) for (i = 0; i < PetersonYieldLockMemoryFence.MAX; i++) { PetersonYieldLockMemoryFence.ans++; } // Release the lock PetersonYieldLockMemoryFence.unlock(self); }); } // Main function static main() { // Create two threads (both run func) const t1 = new Thread(() => PetersonYieldLockMemoryFence.func(0)); const t2 = new Thread(() => PetersonYieldLockMemoryFence.func(1)); // Start the threads t1.start(); t2.start(); // Wait for the threads to end. setTimeout(() => { console.log('Actual Count: ' + PetersonYieldLockMemoryFence.ans + ' | Expected Count: ' + PetersonYieldLockMemoryFence.MAX * 2); } 1000); // Delay for a while to ensure threads finish } } // Define a simple Thread class for simulation class Thread { constructor(func) { this.func = func; } start() { this.func(); } } // Run the main function PetersonYieldLockMemoryFence.main();
// mythread.h (A wrapper header file with assert statements) #ifndef __MYTHREADS_h__ #define __MYTHREADS_h__ #include
// mythread.h (A wrapper header file with assert // statements) #ifndef __MYTHREADS_h__ #define __MYTHREADS_h__ #include
import threading import ctypes # Function to lock a thread lock def Thread_lock(lock): lock.acquire() # Acquire the lock # No need for assert in Python acquire will raise an exception if it fails # Function to unlock a thread lock def Thread_unlock(lock): lock.release() # Release the lock # No need for assert in Python release will raise an exception if it fails # Function to create a thread def Thread_create(target args=()): thread = threading.Thread(target=target args=args) thread.start() # Start the thread # No need for assert in Python thread.start() will raise an exception if it fails # Function to join a thread def Thread_join(thread): thread.join() # Wait for the thread to finish # No need for assert in Python thread.join() will raise an exception if it fails
Kimenet:
Thread Entered: 1
Thread Entered: 0
Actual Count: 2000000000 | Expected Count: 2000000000
