A Java FlowLayout osztály a komponensek sorba rendezésére szolgál, egymás után (folyamatba). Ez az applet vagy panel alapértelmezett elrendezése.
A FlowLayout osztály mezői
A FlowLayout osztály konstruktőrei
Példa a FlowLayout osztályra: FlowLayout() konstruktor használata
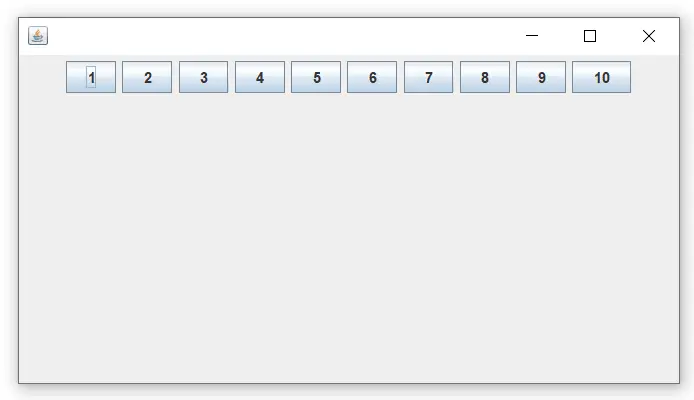
Fájl név: FlowLayoutExample.java
// import statements import java.awt.*; import javax.swing.*; public class FlowLayoutExample { JFrame frameObj; // constructor FlowLayoutExample() { // creating a frame object frameObj = new JFrame(); // creating the buttons JButton b1 = new JButton('1'); JButton b2 = new JButton('2'); JButton b3 = new JButton('3'); JButton b4 = new JButton('4'); JButton b5 = new JButton('5'); JButton b6 = new JButton('6'); JButton b7 = new JButton('7'); JButton b8 = new JButton('8'); JButton b9 = new JButton('9'); JButton b10 = new JButton('10'); // adding the buttons to frame frameObj.add(b1); frameObj.add(b2); frameObj.add(b3); frameObj.add(b4); frameObj.add(b5); frameObj.add(b6); frameObj.add(b7); frameObj.add(b8); frameObj.add(b9); frameObj.add(b10); // parameter less constructor is used // therefore, alignment is center // horizontal as well as the vertical gap is 5 units. frameObj.setLayout(new FlowLayout()); frameObj.setSize(300, 300); frameObj.setVisible(true); } // main method public static void main(String argvs[]) { new FlowLayoutExample(); } } Kimenet:
Példa a FlowLayout osztályra: FlowLayout(int align) konstruktor használata
Fájl név: MyFlowLayout.java
import java.awt.*; import javax.swing.*; public class MyFlowLayout{ JFrame f; MyFlowLayout(){ f=new JFrame(); JButton b1=new JButton('1'); JButton b2=new JButton('2'); JButton b3=new JButton('3'); JButton b4=new JButton('4'); JButton b5=new JButton('5'); // adding buttons to the frame f.add(b1); f.add(b2); f.add(b3); f.add(b4); f.add(b5); // setting flow layout of right alignment f.setLayout(new FlowLayout(FlowLayout.RIGHT)); f.setSize(300,300); f.setVisible(true); } public static void main(String[] args) { new MyFlowLayout(); } } Kimenet:
 töltse le ezt a példát
töltse le ezt a példátPélda a FlowLayout osztályra: FlowLayout(int align, int hgap, int vgap) konstruktor használata
Fájl név: FlowLayoutExample1.java
// import statement import java.awt.*; import javax.swing.*; public class FlowLayoutExample1 { JFrame frameObj; // constructor FlowLayoutExample1() { // creating a frame object frameObj = new JFrame(); // creating the buttons JButton b1 = new JButton('1'); JButton b2 = new JButton('2'); JButton b3 = new JButton('3'); JButton b4 = new JButton('4'); JButton b5 = new JButton('5'); JButton b6 = new JButton('6'); JButton b7 = new JButton('7'); JButton b8 = new JButton('8'); JButton b9 = new JButton('9'); JButton b10 = new JButton('10'); // adding the buttons to frame frameObj.add(b1); frameObj.add(b2); frameObj.add(b3); frameObj.add(b4); frameObj.add(b5); frameObj.add(b6); frameObj.add(b7); frameObj.add(b8); frameObj.add(b9); frameObj.add(b10); // parameterized constructor is used // where alignment is left // horizontal gap is 20 units and vertical gap is 25 units. frameObj.setLayout(new FlowLayout(FlowLayout.LEFT, 20, 25)); frameObj.setSize(300, 300); frameObj.setVisible(true); } // main method public static void main(String argvs[]) { new FlowLayoutExample1(); } } Kimenet:

