Bináris fa egy fa típusú nemlineáris adatstruktúra, amelyet elsősorban rendezésre és keresésre használnak, mivel hierarchikus formában tárolják az adatokat. Ebben a részben megtanuljuk a bináris fa adatstruktúra megvalósítása Java nyelven . Ezenkívül rövid leírást ad a bináris fa adatszerkezetéről.
Bináris fa
Bináris fának nevezzük azt a fát, amelyben minden csomópontnak (szülőnek) legfeljebb két gyermekcsomópontja van (bal és jobb). A legfelső csomópontot gyökércsomópontnak nevezzük. Egy bináris fában egy csomópont tartalmazza a bal és a jobb oldali gyermekcsomópont adatait és mutatóját (címét).
betűméretek latexben
A magasság egy bináris fának az a fa gyökerei közötti élek száma és legtávolabbi (legmélyebb) levele. Ha a fa az üres , a magasság az 0 . A csomópont magasságát jelöli h .
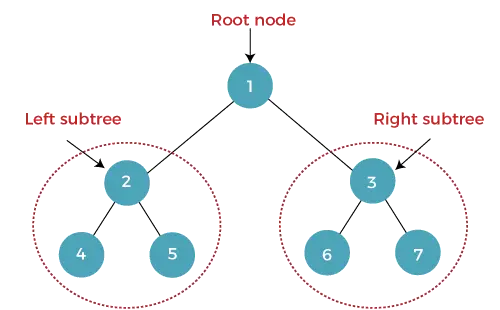
A fenti bináris fa magassága 2.
A levelek és a csomópontok számát a következő képlet segítségével számíthatjuk ki.
- A levél csomópontjainak maximális száma egy bináris fa: 2h
- A csomópontok maximális száma egy bináris fa: 2h+1-1
Ahol h a bináris fa magassága.
Példa a bináris fára

A bináris fa típusai
Az adatszerkezetben a következő típusú bináris fa létezik:
- Teljes/ szigorúan bináris fa
- Teljes bináris fa
- Tökéletes bináris fa
- Egyensúly bináris fa
- Gyökerezett bináris fa
- Degenerált/kóros bináris fa
- Kiterjesztett bináris fa
- Ferde bináris fa
- Balra ferde bináris fa
- Jobbra ferde bináris fa
- Menetes bináris fa
- Egyszálú bináris fa
- Duplaszálú bináris fa
Bináris fa megvalósítása Java nyelven
A bináris fa megvalósításának számos módja van. Ebben a részben bináris fát fogunk megvalósítani a LinkedList adatstruktúra használatával. Ezzel együtt megvalósítjuk a bejárási parancsokat is, megkeresve egy csomópontot, és beillesztünk egy csomópontot egy bináris fába.
Bináris fa megvalósítása LinkedList használatával
Algoritmus
Határozza meg a Node osztályt, amely három attribútumot tartalmaz, nevezetesen: bal és jobb adat. Itt a bal a csomópont bal gyermekét, a jobb pedig a csomópont jobb gyermekét jelenti.
- Csomópont létrehozásakor az adatok átkerülnek a csomópont adatattribútumába, és a bal és a jobb oldal is nullára lesz állítva.
- Határozzon meg egy másik osztályt, amelynek attribútumgyöke van.
- A gyökér a fa gyökércsomópontját jelenti, és nullára inicializálja.
- Ellenőrzi, hogy a gyökér nulla-e, ami azt jelenti, hogy a fa üres. Az új csomópontot rootként adja hozzá.
- Ellenkező esetben rootot ad a sorhoz.
- A változó csomópont az aktuális csomópontot jelöli.
- Először is ellenőrzi, hogy egy csomópontnak van-e bal és jobb gyermeke. Ha igen, akkor mindkét csomópontot hozzáadja a sorhoz.
- Ha a bal oldali gyermek nincs jelen, akkor az új csomópontot bal oldali gyermekként adja hozzá.
- Ha a bal oldal van, akkor az új csomópontot a megfelelő gyermekként adja hozzá.
- Bejárja az egész fát, majd kinyomtatja a bal oldali gyermeket, majd a gyökeret, majd a jobb oldali gyermeket.
BinarySearchTree.java
public class BinarySearchTree { //Represent the node of binary tree public static class Node{ int data; Node left; Node right; public Node(int data){ //Assign data to the new node, set left and right children to null this.data = data; this.left = null; this.right = null; } } //Represent the root of binary tree public Node root; public BinarySearchTree(){ root = null; } //factorial() will calculate the factorial of given number public int factorial(int num) { int fact = 1; if(num == 0) return 1; else { while(num > 1) { fact = fact * num; num--; } return fact; } } //numOfBST() will calculate the total number of possible BST by calculating Catalan Number for given key public int numOfBST(int key) { int catalanNumber = factorial(2 * key)/(factorial(key + 1) * factorial(key)); return catalanNumber; } public static void main(String[] args) { BinarySearchTree bt = new BinarySearchTree(); //Display total number of possible binary search tree with key 5 System.out.println('Total number of possible Binary Search Trees with given key: ' + bt.numOfBST(5)); } } Kimenet:
Binary tree after insertion 1 Binary tree after insertion 2 1 3 Binary tree after insertion 4 2 5 1 3 Binary tree after insertion 4 2 5 1 6 3 7
Bináris fa műveletek
A következő műveletek hajthatók végre egy bináris fán:
- Beillesztés
- Törlés
- Keresés
- Bejárás
Java program csomópont beszúrására a bináris fába
BinaryTreeInsert.java
public class BinaryTreeInsert { public static void main(String[] args) { new BinaryTreeInsert().run(); } static class Node { Node left; Node right; int value; public Node(int value) { this.value = value; } } public void run() { Node rootnode = new Node(25); System.out.println('Building tree with root value ' + rootnode.value); System.out.println('================================='); insert(rootnode, 11); insert(rootnode, 15); insert(rootnode, 16); insert(rootnode, 23); insert(rootnode, 79); } public void insert(Node node, int value) { if (value node.value) { if (node.right != null) { insert(node.right, value); } else { System.out.println(' Inserted ' + value + ' to right of Node ' + node.value); node.right = new Node(value); } } } } Kimenet:
Building tree with root value 25 ================================= Inserted 11 to left of Node 25 Inserted 15 to right of Node 11 Inserted 16 to right of Node 15 Inserted 23 to right of Node 16 Inserted 79 to right of Node 25
Java program csomópont törlésére Java nyelven
Algoritmus
- A gyökértől kezdve keressük meg a legmélyebb és jobb szélső csomópontot a bináris fában és a csomópontot, amelyet törölni szeretnénk.
- Cserélje ki a legmélyebb jobb szélső csomópont adatait a törölni kívánt csomópontra.
- Ezután törölje a legmélyebb jobb szélső csomópontot.
Tekintsük a következő ábrát.

DeleteNode.java
konvertálja a karakterláncot json java-ba
import java.util.LinkedList; import java.util.Queue; public class DeleteNode { // A binary tree node has key, pointer to // left child and a pointer to right child static class Node { int key; Node left, right; // Constructor Node(int key) { this.key = key; left = null; right = null; } } static Node root; static Node temp = root; // Inorder traversal of a binary tree static void inorder(Node temp) { if (temp == null) return; inorder(temp.left); System.out.print(temp.key + ' '); inorder(temp.right); } // Function to delete deepest // element in binary tree static void deleteDeepest(Node root, Node delNode) { Queue q = new LinkedList(); q.add(root); Node temp = null; // Do level order traversal until last node while (!q.isEmpty()) { temp = q.peek(); q.remove(); if (temp == delNode) { temp = null; return; } if (temp.right!=null) { if (temp.right == delNode) { temp.right = null; return; } else q.add(temp.right); } if (temp.left != null) { if (temp.left == delNode) { temp.left = null; return; } else q.add(temp.left); } } } // Function to delete given element // in binary tree static void delete(Node root, int key) { if (root == null) return; if (root.left == null && root.right == null) { if (root.key == key) { root=null; return; } else return; } Queue q = new LinkedList(); q.add(root); Node temp = null, keyNode = null; // Do level order traversal until // we find key and last node. while (!q.isEmpty()) { temp = q.peek(); q.remove(); if (temp.key == key) keyNode = temp; if (temp.left != null) q.add(temp.left); if (temp.right != null) q.add(temp.right); } if (keyNode != null) { int x = temp.key; deleteDeepest(root, temp); keyNode.key = x; } } // Driver code public static void main(String args[]) { root = new Node(10); root.left = new Node(11); root.left.left = new Node(7); root.left.right = new Node(12); root.right = new Node(9); root.right.left = new Node(15); root.right.right = new Node(8); System.out.print('Inorder traversal before deletion: '); inorder(root); //node to delete int key = 7; delete(root, key); System.out.print('
Inorder traversal after deletion: '); inorder(root); } } Kimenet:
Inorder traversal before deletion: 7 11 12 10 15 9 8 Inorder traversal after deletion: 8 11 12 10 15 9
Java program csomópontok keresésére a bináris fában
Algoritmus
- Határozza meg a Node osztályt, amelynek három attribútuma van, nevezetesen: bal és jobb adat. Itt a bal a csomópont bal gyermekét, a jobb pedig a csomópont jobb gyermekét jelenti.
- Csomópont létrehozásakor az adatok átkerülnek a csomópont adatattribútumába, és a bal és a jobb oldal is nullára lesz állítva.
- Határozzon meg egy másik osztályt, amelynek két attribútum gyökér és zászlója van.
- A gyökér a fa gyökércsomópontját jelenti, és nullára inicializálja.
- A Flag segítségével ellenőrizhető, hogy az adott csomópont jelen van-e a fában vagy sem. Kezdetben false értékre lesz állítva.
- Ellenőrzi, hogy a gyökér nulla-e, ami azt jelenti, hogy a fa üres.
- Ha a fa nem üres, akkor összehasonlítja a temp adatait az értékkel. Ha egyenlők, akkor a jelzőt igazra állítja, és visszatér.
- Haladjon be a bal oldali részfán a searchNode() rekurzív meghívásával, és ellenőrizze, hogy az érték megtalálható-e a bal oldali részfában.
- Járja be a jobb oldali részfát a searchNode() rekurzív meghívásával, és ellenőrizze, hogy az érték megtalálható-e a jobb oldali részfában.
SearchBinaryTree.java
public class SearchBinaryTree { //Represent a node of binary tree public static class Node { int data; Node left; Node right; public Node(int data) { //Assign data to the new node, set left and right children to null this.data = data; this.left = null; this.right = null; } } //Represent the root of binary tree public Node root; public static boolean flag = false; public SearchBinaryTree() { root = null; } //searchNode() will search for the particular node in the binary tree public void searchNode(Node temp, int value) { //Check whether tree is empty if(root == null) { System.out.println('Tree is empty'); } else { //If value is found in the given binary tree then, set the flag to true if(temp.data == value) { flag = true; return; } //Search in left subtree if(flag == false && temp.left != null) { searchNode(temp.left, value); } //Search in right subtree if(flag == false && temp.right != null) { searchNode(temp.right, value); } } } public static void main(String[] args) { SearchBinaryTree bt = new SearchBinaryTree(); //Add nodes to the binary tree bt.root = new Node(11); bt.root.left = new Node(8); bt.root.right = new Node(12); bt.root.left.left = new Node(78); bt.root.right.left = new Node(23); bt.root.right.right = new Node(36); //Search for node 5 in the binary tree bt.searchNode(bt.root, 23); if(flag) System.out.println('Element is present in the binary tree.'); else System.out.println('Element is not present in the binary tree.'); } } Kimenet:
Element is present in the binary tree.
Bináris fa bejárása
| Bejárási rendelés | Első látogatás | Második látogatás | Harmadik látogatás |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inorder | Látogassa meg a bal oldali részfát sorrendben | Látogassa meg a gyökércsomópontot | Látogassa meg a jobb oldali részfát sorrendben |
| Előrendelés | Látogassa meg a gyökércsomópontot | Látogassa meg a bal oldali részfát előrendelésben | Látogassa meg a jobb oldali részfát az előrendelésben |
| Levélbeni rendelés | Látogassa meg a bal oldali részfát az utósorban | Látogassa meg a jobb oldali részfát az utósorban | Látogassa meg a gyökércsomópontot |
Megjegyzés: A fenti három bejáráson kívül van egy másik bejárási sorrend, az úgynevezett határátjárás.
Java program a sorrendben, az előrendelésben és az utólagos bejáráshoz
BinaryTree.java
.tif fájl
public class BinaryTree { // first node private Node root; BinaryTree() { root = null; } // Class representing tree nodes static class Node { int value; Node left; Node right; Node(int value) { this.value = value; left = null; right = null; } public void displayData() { System.out.print(value + ' '); } } public void insert(int i) { root = insert(root, i); } //Inserting node - recursive method public Node insert(Node node, int value) { if(node == null){ return new Node(value); } // Move to the left if passed value is // less than the current node if(value node.value) { node.right = insert(node.right, value); } return node; } // Search node in binary search tree public Node find(int searchedValue) { Node current = root; while(current.value != searchedValue) { if(searchedValue = current = current.right; if(current == null) { return null; } } return current; } // For traversing in order public void inOrder(Node node) { if(node != null) { inOrder(node.left); node.displayData(); inOrder(node.right); } } // Preorder traversal public void preOrder(Node node) { if(node != null){ node.displayData(); preOrder(node.left); preOrder(node.right); } } // Postorder traversal public void postOrder(Node node) { if(node != null) { postOrder(node.left); postOrder(node.right); node.displayData(); } } public static void main(String[] args) { BinaryTree bst = new BinaryTree(); bst.insert(34); bst.insert(56); bst.insert(12); bst.insert(89); bst.insert(67); bst.insert(90); System.out.println('Inorder traversal of binary tree'); bst.inOrder(bst.root); System.out.println(); System.out.println('Preorder traversal of binary tree'); bst.preOrder(bst.root); System.out.println(); System.out.println('Postorder traversal of binary tree'); bst.postOrder(bst.root); System.out.println(); } } Kimenet:
Inorder traversal of binary tree 12 34 56 67 89 90 Preorder traversal of binary tree 34 12 56 89 67 90 Postorder traversal of binary tree 12 67 90 89 56 34
A fenti műveletek mellett olyan műveleteket is végrehajthatunk, mint a nagy csomópont, a legkisebb csomópont és az összes csomópont összege.
Java program a bináris fa legnagyobb csomópontjának megtalálásához
LegnagyobbNode.java
public class LargestNode { //Represent the node of binary tree public static class Node { int data; Node left; Node right; public Node(int data) { //Assign data to the new node, set left and right children to null this.data = data; this.left = null; this.right = null; } } //Represent the root of binary tree public Node root; public LargestNode() { root = null; } //largestElement() will find out the largest node in the binary tree public int largestElement(Node temp) { //Check whether tree is empty if(root == null) { System.out.println('Tree is empty'); return 0; } else { int leftMax, rightMax; //Max will store temp's data int max = temp.data; //It will find largest element in left subtree if(temp.left != null){ leftMax = largestElement(temp.left); //Compare max with leftMax and store greater value into max max = Math.max(max, leftMax); } //It will find largest element in right subtree if(temp.right != null){ rightMax = largestElement(temp.right); //Compare max with rightMax and store greater value into max max = Math.max(max, rightMax); } return max; } } public static void main(String[] args) { LargestNode bt = new LargestNode(); //Add nodes to the binary tree bt.root = new Node(90); bt.root.left = new Node(99); bt.root.right = new Node(23); bt.root.left.left = new Node(96); bt.root.right.left = new Node(45); bt.root.right.right = new Node(6); bt.root.right.left = new Node(13); bt.root.right.right = new Node(77); //Display largest node in the binary tree System.out.println('Largest element in the binary tree: ' + bt.largestElement(bt.root)); } } Kimenet:
Largest element in the binary tree: 99
Java program a bináris fa legkisebb csomópontjának megtalálásához
Algoritmus
- Határozza meg a Node osztályt, amelynek három attribútuma van, nevezetesen: adat, bal és jobb. Itt a bal a csomópont bal gyermekét, a jobb pedig a csomópont jobb gyermekét jelenti.
- Csomópont létrehozásakor az adatok átkerülnek a csomópont adatattribútumába, és a bal és a jobb oldal nullára lesz állítva.
- Határozzon meg egy másik osztályt, amelynek attribútumgyöke van.
Gyökér reprezentálja a fa gyökércsomópontját, és nullára inicializálja.
- Ellenőrzi, hogy a gyökér nulla , ami azt jelenti, hogy a fa üres.
- Ha a fa nem üres, definiáljon egy min változót, amely tárolja a temp adatait.
- Keresse meg a bal oldali részfa minimális csomópontját a smallestElement() rekurzív meghívásával. Tárolja ezt az értéket a leftMin-ben. Hasonlítsa össze a min értékét a leftMin értékkel, és tárolja a minimum kettőt min.
- Keresse meg a minimális csomópontot a jobb oldali részfában a smallestElement() rekurzív meghívásával. Tárolja ezt az értéket a rightMin-ben. Hasonlítsa össze a min értékét a rightMin értékkel, és tárolja a maximumot kettőtől minig.
- A végén min a bináris fa legkisebb csomópontja lesz.
SmallestNode.java
public class SmallestNode { //Represent the node of binary tree public static class Node { int data; Node left; Node right; public Node(int data) { //Assign data to the new node, set left and right children to null this.data = data; this.left = null; this.right = null; } } //Represent the root of binary tree public Node root; public SmallestNode() { root = null; } //smallestElement() will find out the smallest node in the binary tree public int smallestElement(Node temp) { //Check whether tree is empty if(root == null) { System.out.println('Tree is empty'); return 0; } else { int leftMin, rightMin; //Min will store temp's data int min = temp.data; //It will find smallest element in left subtree if(temp.left != null) { leftMin = smallestElement(temp.left); //If min is greater than leftMin then store the value of leftMin into min min = Math.min(min, leftMin); } //It will find smallest element in right subtree if(temp.right != null) { rightMin = smallestElement(temp.right); //If min is greater than rightMin then store the value of rightMin into min min = Math.min(min, rightMin); } return min; } } public static void main(String[] args) { SmallestNode bt = new SmallestNode(); //Add nodes to the binary tree bt.root = new Node(9); bt.root.left = new Node(5); bt.root.right = new Node(7); bt.root.left.left = new Node(1); bt.root.right.left = new Node(2); bt.root.right.right = new Node(8); bt.root.right.left = new Node(4); bt.root.right.right = new Node(3); //Display smallest node in the binary tree System.out.println('Smallest element in the binary tree: ' + bt.smallestElement(bt.root)); } } Kimenet:
Smallest element in the binary tree: 1
Java program egy bináris fa maximális szélességének meghatározásához
Algoritmus
- Határozza meg a Node osztályt, amelynek három attribútuma van, nevezetesen: bal és jobb adat. Itt a bal a csomópont bal gyermekét, a jobb pedig a csomópont jobb gyermekét jelenti.
- Csomópont létrehozásakor az adatok átkerülnek a csomópont adatattribútumába, és a bal és a jobb oldal is nullára lesz állítva.
- Határozzon meg egy másik osztályt, amelynek attribútumgyöke van.
Gyökér a fa gyökércsomópontját jelenti, és nullára inicializálja.
- A maxWidth változó a bármely szinten jelenlévő csomópontok maximális számát tárolja.
- A sort a bináris fa szinten történő bejárására használják.
- Ellenőrzi, hogy a gyökér nulla-e, ami azt jelenti, hogy a fa üres.
- Ha nem, adja hozzá a gyökércsomópontot a sorhoz. A nodesInLevel változó nyomon követi az egyes szinteken lévő csomópontok számát.
- Ha a nodesInLevel > 0, távolítsa el a csomópontot a sor elejéről, és adja hozzá a sorhoz a bal és a jobb oldali gyermekét. Az első iteráció során az 1. csomópont eltávolításra kerül, és a hozzá tartozó 2. és 3. csomópontok hozzáadódnak a sorhoz. A második iterációban a 2. csomópont eltávolításra kerül, a 4. és 5. gyermekei hozzáadódnak a sorhoz és így tovább.
- A MaxWidth a max(maxWidth, nodesInLevel) tárolja. Tehát bármely adott időpontban a csomópontok maximális számát fogja képviselni.
- Ez addig fog folytatódni, amíg a fa összes szintjét be nem járja.
BinaryTree.java
import java.util.LinkedList; import java.util.Queue; public class BinaryTree { //Represent the node of binary tree public static class Node { int data; Node left; Node right; public Node(int data) { //Assign data to the new node, set left and right children to null this.data = data; this.left = null; this.right = null; } } //Represent the root of binary tree public Node root; public BinaryTree() { root = null; } //findMaximumWidth() will find out the maximum width of the given binary tree public int findMaximumWidth() { int maxWidth = 0; //Variable nodesInLevel keep tracks of number of nodes in each level int nodesInLevel = 0; //queue will be used to keep track of nodes of tree level-wise Queue queue = new LinkedList(); //Check if root is null, then width will be 0 if(root == null) { System.out.println('Tree is empty'); return 0; } else { //Add root node to queue as it represents the first level queue.add(root); while(queue.size() != 0) { //Variable nodesInLevel will hold the size of queue i.e. number of elements in queue nodesInLevel = queue.size(); //maxWidth will hold maximum width. //If nodesInLevel is greater than maxWidth then, maxWidth will hold the value of nodesInLevel maxWidth = Math.max(maxWidth, nodesInLevel); //If variable nodesInLevel contains more than one node //then, for each node, we'll add left and right child of the node to the queue while(nodesInLevel > 0) { Node current = queue.remove(); if(current.left != null) queue.add(current.left); if(current.right != null) queue.add(current.right); nodesInLevel--; } } } return maxWidth; } public static void main(String[] args) { BinaryTree bt = new BinaryTree(); //Add nodes to the binary tree bt.root = new Node(1); bt.root.left = new Node(2); bt.root.right = new Node(3); bt.root.left.left = new Node(4); bt.root.left.right = new Node(5); bt.root.right.left = new Node(6); bt.root.right.right = new Node(7); bt.root.left.left.left = new Node(8); //Display the maximum width of given tree System.out.println('Maximum width of the binary tree: ' + bt.findMaximumWidth()); } } Kimenet:
Maximum width of the binary tree: 4
