Létrehozhatunk egy java programot a tömbelemek rendezésére a kiválasztás rendezés segítségével. A kiválasztási rendezési algoritmusban megkeressük a legalacsonyabb elemet, és elrendezzük a megfelelő helyre. Az aktuális elemet felcseréljük a következő legalacsonyabb számmal.
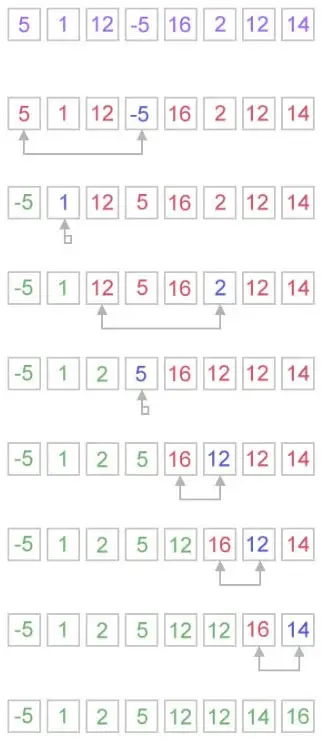
Hogyan működik a kiválasztási rendezés?
A kiválasztási rendezési algoritmus nagyon egyszerű módon működik. Két altömböt tart fenn az adott tömbhöz.
10/100.00
- Az alcsoport már rendezve van.
- A második alcsoport pedig rendezetlen.
A kiválasztási rendezés minden iterációja során a rendszer egy elemet kiválaszt a rendezetlen altömbből, és áthelyezi a rendezett altömbbe.
színész zeenat aman
arr[] = 25 35 45 12 65 10 // Find the minimum element in arr[0...5] and place it at beginning. 10 25 35 45 12 65 // Find the minimum element in arr[1...5] and place it at beginning of arr[1...5] 10 12 25 35 45 65 // Find the minimum element in arr[2...5] and place it at beginning of arr[2...5] No, you can see that the array is already sorted. 10 12 25 35 45 65
Idő összetettsége
Legjobb: ?(n^2)Átlagos: ?(n^2)
Legrosszabb: O(n^2)
A tér összetettsége
O(1)Kijelölés Sort Java példa
public class SelectionSortExample { public static void selectionSort(int[] arr){ for (int i = 0; i <arr.length - 1; i++) { int index="i;" for (int j="i" + < arr.length; j++){ if (arr[j] arr[index]){ lowest } smallernumber="arr[index];" arr[index]="arr[i];" arr[i]="smallerNumber;" public static void main(string a[]){ int[] arr1="{9,14,3,2,43,11,58,22};" system.out.println('before selection sort'); for(int i:arr1){ system.out.print(i+' '); system.out.println(); selectionsort(arr1); sorting array using sort system.out.println('after pre> <p>Output:</p> <pre> Before Selection Sort 9 14 3 2 43 11 58 22 After Selection Sort 2 3 9 11 14 22 43 58 </pre> <h2>Selection Sort in Java (Another way)</h2> <p>You can also use a method where array is not predefined. Here, user has to put the elements as input.</p> <p>In the following Java program, we ask user to enter the array elements or number, now compare the array's element and start swapping with the variable temp. Put the first element in the temp and the second element in the first, and then temp in the second number and continue for the next match to sort the whole array in ascending order.</p> <pre> import java.util.Scanner; public class SelectionSortExample2 { public static void main(String args[]) { int size, i, j, temp; int arr[] = new int[50]; Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.print('Enter Array Size : '); size = scan.nextInt(); System.out.print('Enter Array Elements : '); for(i=0; i<size; i++) { arr[i]="scan.nextInt();" } system.out.print('sorting array using selection sort technique..
'); for(i="0;" i<size; for(j="i+1;" j arr[j]) temp="arr[i];" arr[j]="temp;" system.out.print('now the after sorting is :
'); system.out.print(arr[i]+ ' '); < pre> <p>Output:</p> <strong> Use image SelectionSort</strong> </size;></pre></arr.length> Kijelölések rendezése Java nyelven (egy másik módszer)
Használhat olyan módszert is, ahol a tömb nincs előre definiálva. Itt a felhasználónak be kell írnia az elemeket bemenetként.
A következő Java programban megkérjük a felhasználót, hogy adja meg a tömb elemeit vagy számát, most hasonlítsa össze a tömb elemét, és kezdje el a cserét a temp változóval. Tegye az első elemet a temp, a második elemet az elsőbe, majd a temp a második számba, és folytassa a következő egyezéssel, hogy az egész tömb növekvő sorrendben legyen rendezve.
import java.util.Scanner; public class SelectionSortExample2 { public static void main(String args[]) { int size, i, j, temp; int arr[] = new int[50]; Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.print('Enter Array Size : '); size = scan.nextInt(); System.out.print('Enter Array Elements : '); for(i=0; i<size; i++) { arr[i]="scan.nextInt();" } system.out.print(\'sorting array using selection sort technique..
\'); for(i="0;" i<size; for(j="i+1;" j arr[j]) temp="arr[i];" arr[j]="temp;" system.out.print(\'now the after sorting is :
\'); system.out.print(arr[i]+ \' \'); < pre> <p>Output:</p> <strong> Use image SelectionSort</strong> </size;>