Adott egy n szám, keresse meg az összes 2n hosszúságú bináris sorozatot úgy, hogy az első n bit összege megegyezzen az utolsó n bit összegével.
Példák:
abs c kód
Input: N = 2 Output: 0101 1111 1001 0110 0000 1010 Input: N = 3 Output: 011011 001001 011101 010001 101011 111111 110011 101101 100001 110101 001010 011110 010010 001100 000000 010100 101110 100010 110110 100100
Az ötlet az, hogy rögzítjük az első és az utolsó bitet, majd ismételjük meg a maradék 2*(n-1) bitet. Négy lehetőség van az első és az utolsó bit javítására -
- Az első és az utolsó bit 1 maradék n - mindkét oldalon 1 bitnek ugyanannyinak kell lennie.
- Az első és az utolsó bit 0, a fennmaradó n - 1 bitnek mindkét oldalon ugyanannyinak kell lennie.
- Az első bit 1, az utolsó bit pedig 0, a bal oldalon fennmaradó n - 1 bit összegének 1-gyel kisebbnek kell lennie, mint a jobb oldalon lévő n-1 bit összegének.
- Az első bit 0, az utolsó bit pedig 1, a maradék n - 1 bit összege a bal oldalon 1-gyel több, mint a jobb oldalon lévő n-1 bit összege.
Alább látható a fenti ötlet megvalósítása -
// C++ program to print even length binary sequences // whose sum of first and second half bits is same #include
// Java program to print even length binary // sequences whose sum of first and second // half bits is same import java.io.*; import java.util.*; class GFG { // Function to print even length binary sequences // whose sum of first and second half bits is same // diff --> difference between sums of first n bits // and last n bits // out --> output array // start --> starting index // end --> ending index static void findAllSequences(int diff char out[] int start int end) { // We can't cover difference of more // than n with 2n bits if (Math.abs(diff) > (end - start + 1) / 2) return; // if all bits are filled if (start > end) { // if sum of first n bits and // last n bits are same if (diff == 0) { System.out.print(out); System.out.print(' '); } return; } // fill first bit as 0 and last bit as 1 out[start] = '0'; out[end] = '1'; findAllSequences(diff + 1 out start + 1 end - 1); // fill first and last bits as 1 out[start] = out[end] = '1'; findAllSequences(diff out start + 1 end - 1); // fill first and last bits as 0 out[start] = out[end] = '0'; findAllSequences(diff out start + 1 end - 1); // fill first bit as 1 and last bit as 0 out[start] = '1'; out[end] = '0'; findAllSequences(diff - 1 out start + 1 end - 1); } // Driver program public static void main (String[] args) { // input number int n = 2; // allocate string containing 2*n characters char[] out = new char[2 * n + 1]; // null terminate output array out[2 * n] = '�'; findAllSequences(0 out 0 2*n - 1); } } // This code is contributed by Pramod Kumar
# Python3 program to print even length binary sequences # whose sum of first and second half bits is same # Function to print even length binary sequences # whose sum of first and second half bits is same # diff --> difference between sums of first n bits # and last n bits # out --> output array # start --> starting index # end --> ending index def findAllSequences(diff out start end): # We can't cover difference of more than n with 2n bits if (abs(diff) > (end - start + 1) // 2): return; # if all bits are filled if (start > end): # if sum of first n bits and last n bits are same if (diff == 0): print(''.join(list(out))end=' '); return; # fill first bit as 0 and last bit as 1 out[start] = '0'; out[end] = '1'; findAllSequences(diff + 1 out start + 1 end - 1); # fill first and last bits as 1 out[start] = out[end] = '1'; findAllSequences(diff out start + 1 end - 1); # fill first and last bits as 0 out[start] = out[end] = '0'; findAllSequences(diff out start + 1 end - 1); # fill first bit as 1 and last bit as 0 out[start] = '1'; out[end] = '0'; findAllSequences(diff - 1 out start + 1 end - 1); # Driver program # input number n = 2; # allocate string containing 2*n characters out=['']*(2*n); findAllSequences(0 out 0 2*n - 1); # This code is contributed by mits
// C# program to print even length binary // sequences whose sum of first and second // half bits is same using System; class GFG { // Function to print even length binary // sequences whose sum of first and // second half bits is same // diff --> difference between sums of // first n bits // and last n bits // out --> output array // start --> starting index // end --> ending index static void findAllSequences(int diff char []outt int start int end) { // We can't cover difference of // more than n with 2n bits if (Math.Abs(diff) > (end - start + 1) / 2) return; // if all bits are filled if (start > end) { // if sum of first n bits and // last n bits are same if (diff == 0) { Console.Write(outt); Console.Write(' '); } return; } // fill first bit as 0 and last bit // as 1 outt[start] = '0'; outt[end] = '1'; findAllSequences(diff + 1 outt start + 1 end - 1); // fill first and last bits as 1 outt[start] = outt[end] = '1'; findAllSequences(diff outt start + 1 end - 1); // fill first and last bits as 0 outt[start] = outt[end] = '0'; findAllSequences(diff outt start + 1 end - 1); // fill first bit as 1 and last // bit as 0 outt[start] = '1'; outt[end] = '0'; findAllSequences(diff - 1 outt start + 1 end - 1); } // Driver program public static void Main () { // input number int n = 2; // allocate string containing 2*n // characters char []outt = new char[2 * n + 1]; // null terminate output array outt[2 * n] = '�'; findAllSequences(0 outt 0 2*n - 1); } } // This code is contributed by nitin mittal.
// PHP program to print even length binary sequences // whose sum of first and second half bits is same // Function to print even length binary sequences // whose sum of first and second half bits is same // diff --> difference between sums of first n bits // and last n bits // out --> output array // start --> starting index // end --> ending index function findAllSequences($diff $out $start $end) { // We can't cover difference of more than n with 2n bits if (abs($diff) > (int)(($end - $start + 1) / 2)) return; // if all bits are filled if ($start > $end) { // if sum of first n bits and last n bits are same if ($diff == 0) print(implode(''$out).' '); return; } // fill first bit as 0 and last bit as 1 $out[$start] = '0'; $out[$end] = '1'; findAllSequences($diff + 1 $out $start + 1 $end - 1); // fill first and last bits as 1 $out[$start] = $out[$end] = '1'; findAllSequences($diff $out $start + 1 $end - 1); // fill first and last bits as 0 $out[$start] = $out[$end] = '0'; findAllSequences($diff $out $start + 1 $end - 1); // fill first bit as 1 and last bit as 0 $out[$start] = '1'; $out[$end] = '0'; findAllSequences($diff - 1 $out $start + 1 $end - 1); } // Driver program // input number $n = 2; // allocate string containing 2*n characters $out=array_fill(02*$n''); findAllSequences(0 $out 0 2*$n - 1); // This code is contributed by chandan_jnu ?> <script> // JavaScript program to print even length binary // sequences whose sum of first and second // half bits is same // Function to print even length binary // sequences whose sum of first and // second half bits is same // diff --> difference between sums of // first n bits // and last n bits // out --> output array // start --> starting index // end --> ending index function findAllSequences(diff outt start end) { // We can't cover difference of // more than n with 2n bits if (Math.abs(diff) > parseInt((end - start + 1) / 2 10)) return; // if all bits are filled if (start > end) { // if sum of first n bits and // last n bits are same if (diff == 0) { document.write(outt.join('')); document.write(' '); } return; } // fill first bit as 0 and last bit // as 1 outt[start] = '0'; outt[end] = '1'; findAllSequences(diff + 1 outt start + 1 end - 1); // fill first and last bits as 1 outt[start] = outt[end] = '1'; findAllSequences(diff outt start + 1 end - 1); // fill first and last bits as 0 outt[start] = outt[end] = '0'; findAllSequences(diff outt start + 1 end - 1); // fill first bit as 1 and last // bit as 0 outt[start] = '1'; outt[end] = '0'; findAllSequences(diff - 1 outt start + 1 end - 1); } // input number let n = 2; // allocate string containing 2*n // characters let outt = new Array(2 * n + 1); // null terminate output array outt[2 * n] = '�'; findAllSequences(0 outt 0 2*n - 1); </script>
Kimenet
0101 1111 1001 0110 0000 1010
Időbeli összetettség: O((4 ^ N )* N)
4^N a 4 rekurzív hívás miatt és N (2N-ről egyszerűsítve) a 2N méretű karakterláncok nyomtatására fordított időért
Kiegészítő tér: ON)
Létezik egy másik megközelítés, amellyel az összes lehetséges n hosszúságú karakterláncot előállítjuk, és egy listában tároljuk az összegüket reprezentáló indexen. Utána végigfutjuk az egyes listákat, és előállítjuk a 2n méretű karakterláncokat úgy, hogy mindegyik karakterláncot kinyomtatjuk a listában szereplő összes többi karakterlánccal, amely összeadja ugyanazt az értéket.
C++// C++ program to implement the approach #include
// Java program to implement the approach import java.util.*; class GFG { // function that finds all the subsequences static void findAllSequences(int n) { ArrayList<ArrayList<String> > sumToString = new ArrayList<ArrayList<String> >(); for (int i = 0; i < n + 1; i++) { sumToString.add( new ArrayList<String>()); // list of strings // where index // represents sum } generateSequencesWithSum( n sumToString new ArrayList<String>() 0); permuteSequences(sumToString); } static void generateSequencesWithSum( int n ArrayList<ArrayList<String> > sumToString ArrayList<String> sequence int sumSoFar) { // Base case if there are no more binary digits to // include if (n == 0) { // add permutation to list of sequences with sum // corresponding to index String seq = ''; for (int i = 0; i < sequence.size(); i++) { seq = seq + sequence.get(i); } ArrayList<String> x = sumToString.get(sumSoFar); x.add(seq); sumToString.set(sumSoFar x); return; } // Generate sequence +0 sequence.add('0'); generateSequencesWithSum(n - 1 sumToString sequence sumSoFar); sequence.remove(0); // Generate sequence +1 sequence.add('1'); generateSequencesWithSum(n - 1 sumToString sequence sumSoFar + 1); sequence.remove(0); } // function to form permutations of the sequences static void permuteSequences( ArrayList<ArrayList<String> > sumToString) { // There are 2^n substring in this list of lists for (int sumIndexArr = 0; sumIndexArr < sumToString.size(); sumIndexArr++) { // Append for (int sequence1 = 0; sequence1 < sumToString.get(sumIndexArr).size(); sequence1++) { for (int sequence2 = 0; sequence2 < sumToString.get(sumIndexArr).size(); sequence2++) { if (sumIndexArr == sumToString.size() - 1 && sequence1 == sumToString .get(sumIndexArr) .size() - 1 && sequence2 == sumToString .get(sumIndexArr) .size() - 1) { System.out.print('1111'); } else { System.out.println( sumToString.get(sumIndexArr) .get(sequence1) + sumToString.get(sumIndexArr) .get(sequence2)); } } } } } // Driver Code public static void main(String[] args) { // Function Call findAllSequences(2); } // this code is contributed by phasing17 }
def findAllSequences(n): sumToString = [[] for x in range(n+1)] # list of strings where index represents sum generateSequencesWithSum(n sumToString [] 0) permuteSequences(sumToString) def generateSequencesWithSum(n sumToString sequence sumSoFar): #Base case if there are no more binary digits to include if n == 0: sumToString[sumSoFar].append(''.join(sequence)) #add permutation to list of sequences with sum corresponding to index return #Generate sequence +0 sequence.append('0') generateSequencesWithSum(n-1 sumToString sequence sumSoFar) sequence.pop() #Generate sequence +1 sequence.append('1') generateSequencesWithSum(n-1 sumToString sequence sumSoFar+1) sequence.pop() def permuteSequences(sumToString): #There are 2^n substring in this list of lists for sumIndexArr in sumToString: # Append for sequence1 in sumIndexArr: for sequence2 in sumIndexArr: print(sequence1 + sequence2) findAllSequences(2) #Contribution by Xavier Jean Baptiste
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; class GFG { static void findAllSequences(int n) { List<List<string>> sumToString = new List<List<string>>(); for(int i = 0; i < n + 1; i++) { sumToString.Add(new List<string>()); // list of strings where index represents sum } generateSequencesWithSum(n sumToString new List<string>() 0); permuteSequences(sumToString); } static void generateSequencesWithSum(int n List<List<string>> sumToString List<string> sequence int sumSoFar) { // Base case if there are no more binary digits to include if(n == 0) { //add permutation to list of sequences with sum corresponding to index string seq = ''; for(int i = 0; i < sequence.Count; i++) { seq = seq + sequence[i]; } sumToString[sumSoFar].Add(seq); return; } // Generate sequence +0 sequence.Add('0'); generateSequencesWithSum(n-1 sumToString sequence sumSoFar); sequence.RemoveAt(0); // Generate sequence +1 sequence.Add('1'); generateSequencesWithSum(n-1 sumToString sequence sumSoFar+1); sequence.RemoveAt(0); } static void permuteSequences(List<List<string>> sumToString) { // There are 2^n substring in this list of lists for(int sumIndexArr = 0; sumIndexArr < sumToString.Count; sumIndexArr++) { // Append for(int sequence1 = 0; sequence1 < sumToString[sumIndexArr].Count; sequence1++) { for(int sequence2 = 0; sequence2 < sumToString[sumIndexArr].Count; sequence2++) { if(sumIndexArr == sumToString.Count-1 && sequence1 == sumToString[sumIndexArr].Count-1 && sequence2 == sumToString[sumIndexArr].Count-1) { Console.Write('1111'); } else { Console.WriteLine(sumToString[sumIndexArr][sequence1] + sumToString[sumIndexArr][sequence2]); } } } } } static void Main() { findAllSequences(2); } } // This code is contributed by divyesh072019.
<script> function findAllSequences(n) { let sumToString = []; for(let i = 0; i < n + 1; i++) { sumToString.push([]); // list of strings where index represents sum } generateSequencesWithSum(n sumToString [] 0); permuteSequences(sumToString); } function generateSequencesWithSum(n sumToString sequence sumSoFar) { // Base case if there are no more binary digits to include if(n == 0) { //add permutation to list of sequences with sum corresponding to index sumToString[sumSoFar].push(sequence.join('')); return; } // Generate sequence +0 sequence.push('0'); generateSequencesWithSum(n-1 sumToString sequence sumSoFar); sequence.shift(); // Generate sequence +1 sequence.push('1'); generateSequencesWithSum(n-1 sumToString sequence sumSoFar+1); sequence.shift(); } function permuteSequences(sumToString) { // There are 2^n substring in this list of lists for(let sumIndexArr = 0; sumIndexArr < sumToString.length; sumIndexArr++) { // Append for(let sequence1 = 0; sequence1 < sumToString[sumIndexArr].length; sequence1++) { for(let sequence2 = 0; sequence2 < sumToString[sumIndexArr].length; sequence2++) { if(sumIndexArr == sumToString.length-1 && sequence1 == sumToString[sumIndexArr].length-1 && sequence2 == sumToString[sumIndexArr].length-1) { document.write('1111'); } else { document.write(sumToString[sumIndexArr][sequence1] + sumToString[sumIndexArr][sequence2] + ''); } } } } } findAllSequences(2); // This code is contributed by decode2207. </script>
Kimenet
0000 0101 0110 1001 1010 1111
Időbeli komplexitás elemzése:
generSequencesWithSum = O((2N)*N)
- 2N: N méretű bináris karakterláncok összes permutációját generáljuk
- N: konvertálja a karakterek listáját karaktersorozattá, és tárolja tömbben. Ez alapesetben történik.
permuteSequences = O((2N) * N!/(N/2)!2*N)
- 2N: iteráljuk az összes n méretű karakterláncot
- N!/(N/2)!2: Ezt kissé nehéz megmagyarázni
vegyük példának N = 2-t. A lehetséges n méretű sorozatok tömbje a következő lenne:
| tömb index | 1 | 2 | |
| karakterláncok listája | 00 | 0110 | 11 |
A karakterláncok listájában, amelyeknek az index az összegét jelenti, megkapjuk a 2n méretű karakterláncok számát az 'n select k' képlet segítségével. A mi esetünkben ez nCk *nCk lenne, ahol k az 1-ek számát jelenti a 2n méretű karakterlánc mindkét felében:
k = 0 van (2C0)^2 = 1 karakterlánc (0000)
k = 1 van (2C1)^2 karakterlánc = 4 karakterlánc(0101 0110 1001 1010)
k = 2 van (2c2)^2 = 1 karakterlánc (1111)
betűtípusok a gimp számára
A leghosszabb karakterlánc-listánkat akkor kapjuk, ha k = N/2NCN/2= N!/[(N/2)! * (N - N/2)!] amely leegyszerűsítiNCN/2= N!/(N/2)!2
Ezért minden egyes elemnél legfeljebb végig kell ismételnünkNCN/22N hosszúságú húrok kialakítására
Formális bizonyítás nélkül, ha 2^N-t és N-t ábrázolunk!/(N/2)!2látjuk, hogy 2Ngyorsabb növekedési ütemű, mint az utóbbi. Ezért O(2N* N!/(N/2)2)< O(2N*2N) = O(22n) = O(4N)
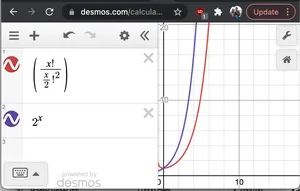 2^x és nC(n/2) grafikonja
2^x és nC(n/2) grafikonja- N: minden 2N méretű karakterláncot ki kell nyomtatnunk
Végül figyelmen kívül hagyhatjuk a generSequencesWithSum időbonyolultságát, mivel a permuteSequence a vezető kifejezés
Időbeli összetettség: O(2N* N!/(N/2)!2* N) (jobb, mint az O(4^N) * N első megoldása, lásd a fenti magyarázatot további részletekért)
Segédtér : O(2N), mert minden N méretű bináris karakterlánc-permutációt tárolunk
windows parancs arp
#include
import java.util.*; class GFG { static class FirstHalf { String data; int sum; FirstHalf(String data int sum) { this.data = data; this.sum = sum; } } //MAP: Key -> sum of bits; Value -> All possible permutation with respective sum static Map<Integer ArrayList<String>> map = new HashMap<>(); //first N-half bits static List<FirstHalf> firstHalf = new ArrayList<>(); //function to find sum of the bits from a String public static int sumOfString(String s) { int sum = 0; //ex: converts '1' to 1 -> (ASCII('1') - ASCII('0') = 1) for(char c: s.toCharArray()) { sum += c - '0'; } return sum; } public static void perm(String p char[] bin int level int n) { //p: processed string(processed permutation at current level) //bin: {'0' '1'} //l: current level of recursion tree (leaf/solution level = 0) //n: total levels if(level == 0) { //at solution level find sum of the current permutation int sum = sumOfString(p); //store current permutation to firstHalf list firstHalf.add(new FirstHalf(p sum)); //put current permutation to its respective sum value map.putIfAbsent(sum new ArrayList<String>()); map.get(sum).add(p); return; } //generate calls for permutation //working: first solution with all 0s then replacing last 0 with 1 and so on... for(char c: bin) { perm(p+c bin level-1 n); } } public static void result() { int i = 0; for(FirstHalf first: firstHalf) { //for each firstHalf string //find sum of the bits of current string int sum = first.sum; //retrieve respective secondHalf from map based on sum key ArrayList<String> secondHalf = map.get(sum); for(String second: secondHalf) { //append first and second half and print System.out.print(first.data+second+' '); //after every 6 solution line is changed in output //only for formatting below lines could be removed i++; if(i % 6 == 0) System.out.println(); } } } public static void main(String[] args) { char[] up = {'0' '1'}; int n = 2; perm('' up n n); result(); } } //Code contributed by Animesh Singh
# Python code implementation class FirstHalf: def __init__(self data sum): self.data = data self.sum = sum # MAP: Key -> sum of bits; Value -> All possible permutation with respective sum map = {} # first N-half bits firstHalf = [] # function to find sum of the bits from a String def sumOfString(s): sum = 0 # ex: converts '1' to 1 -> (ASCII('1') - ASCII('0') = 1) for i in range(len(s)): sum += ord(s[i]) - ord('0') return sum def perm(p bin level n): # p: processed string(processed permutation at current level) # bin: ['0' '1'] # l: current level of recursion tree (leaf/solution level = 0) # n: total levels if level == 0: # at solution level find sum of the current permutation sum = sumOfString(p) # store current permutation to firstHalf list firstHalf.append(FirstHalf(p sum)) # put current permutation to its respective sum value if sum not in map: map[sum] = [] map[sum].append(p) return # generate calls for permutation # working: first solution with all 0s then replacing last 0 with 1 and so on... for i in range(len(bin)): perm(p+bin[i] bin level-1 n) def result(): i = 0 for j in range(len(firstHalf)): # for each firstHalf string # find sum of the bits of current string sum = firstHalf[j].sum # retrieve respective secondHalf from map based on sum key secondHalf = map[sum] for k in range(len(secondHalf)): # append first and second half and print print(firstHalf[j].data + secondHalf[k] + ' ' end='') # after every 6 solution line is changed in output # only for formatting below lines could be removed i = i + 1 if(i % 6 == 0): print('n') up = ['0' '1'] n = 2 perm('' up n n) result() # The code is contributed by Nidhi goel.
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; class FirstHalf { public string data; public int sum; public FirstHalf(string data int sum) { this.data = data; this.sum = sum; } } class Gfg { // MAP: Key -> sum of bits; Value -> All possible permutation with respective sum static Dictionary<int List<string>> mp = new Dictionary<int List<string>>(); // first N-half bits static List<FirstHalf> firstHalf = new List<FirstHalf>(); // function to find sum of the bits from a String static int sumOfString(string s) { int sum = 0; // ex: converts '1' to 1 -> (ASCII('1') - ASCII('0') = 1) foreach (char c in s) { sum += (c - '0'); } return sum; } static void perm(string p char[] bin int level int n) { // p: processed string(processed permutation at current level) // bin: {'0' '1'} // l: current level of recursion tree (leaf/solution level = 0) // n: total levels if (level == 0) { // at solution level find sum of the current permutation int sum = sumOfString(p); // store current permutation to firstHalf list firstHalf.Add(new FirstHalf(p sum)); // put current permutation to its respective sum value if (mp.ContainsKey(sum)) { mp[sum].Add(p); } else { mp.Add(sum new List<string> { p }); } return; } // generate calls for permutation // working: first solution with all 0s // then replacing last 0 with 1 and so on... for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { char c = bin[i]; perm(p + c bin level - 1 n); } } static void result() { int i = 0; foreach (FirstHalf first in firstHalf) { // for each firstHalf string // find sum of the bits of current string int sum = first.sum; // retrieve respective secondHalf from map based on sum key List<string> secondHalf = mp[sum]; foreach (string second in secondHalf) { // append first and second half and print Console.Write(first.data + second + ' '); // after every 6 solution line is changed in output // only for formatting below lines could be removed i++; if (i % 6 == 0) Console.WriteLine(); } } } static void Main(string[] args) { char[] up = { '0' '1' }; int n = 2; string x = ''; perm(x up n n); result(); } }
class FirstHalf { constructor(data sum) { this.data = data; this.sum = sum; } } // MAP: Key -> sum of bits; Value -> All possible permutation with respective sum const map = new Map(); // first N-half bits const firstHalf = []; // function to find sum of the bits from a String function sumOfString(s) { let sum = 0; //ex: converts '1' to 1 -> (ASCII('1') - ASCII('0') = 1) for(let i = 0; i < s.length; i++) { sum += s.charCodeAt(i) - '0'.charCodeAt(0); } return sum; } function perm(p bin level n) { // p: processed string(processed permutation at current level) // bin: ['0' '1'] // l: current level of recursion tree (leaf/solution level = 0) // n: total levels if(level == 0) { // at solution level find sum of the current permutation let sum = sumOfString(p); // store current permutation to firstHalf list firstHalf.push(new FirstHalf(p sum)); // put current permutation to its respective sum value if(!map.has(sum)) map.set(sum []); map.get(sum).push(p); return; } // generate calls for permutation // working: first solution with all 0s then replacing last 0 with 1 and so on... for(let i = 0; i < bin.length; i++) { perm(p+bin[i] bin level-1 n); } } function result() { let i = 0; for(let j = 0; j < firstHalf.length; j++) { // for each firstHalf string // find sum of the bits of current string let sum = firstHalf[j].sum; // retrieve respective secondHalf from map based on sum key let secondHalf = map.get(sum); for(let k = 0; k < secondHalf.length; k++) { // append first and second half and print process.stdout.write(firstHalf[j].data + secondHalf[k] + ' '); // after every 6 solution line is changed in output // only for formatting below lines could be removed i++; if(i % 6 == 0) process.stdout.write('n'); } } } const up = ['0' '1']; const n = 2; perm('' up n n); result();
Kimenet
0000 0101 0110 1001 1010 1111
Algoritmus:
1. Generáljon minden n méretű bináris permutációt
2. Számítsa ki az egyes permutációk bitjeinek összegét, és emlékezzen rá a második felére
[például: n=2 esetén ne feledje, hogy van két olyan karakterlánc, amelyek összege = 1, azaz '01' '10' ]
3. Iterálja az összes generált permutációt, és mindegyikhez fűzze hozzá a második felét a bitek összegének megfelelően
Időbeli komplexitás elemzése:
rendezett tömblista java
sumOfString() = O(N) : minden bit bejárása és összeadása
perm() = O(2N*N)
2N * N: létrehozzuk az N méretű bináris bitek összes permutációját, és megtaláljuk a bitek összegét az egyes permutációkhoz
eredmény() = O((2N) * (N!/(N/2)!)2)
2N: Iteráljuk az összes lehetséges N méretű permutációt (első fele)
NCN/2 = N!/(N/2)!2: (maximális méret második fele) : magyarázat lent:
Vegyünk példának N = 4-et.
//Hash-Map úgy néz ki
0 -> [0000] ................................(lista-méret: 4C0 = 1)
1 -> [0001 0010 0100 1000] .................................(lista mérete: 4C1 = 4)
2 -> [0011 0101 0110 1001 1010 1100] .................................(lista mérete: 4C2 = 6)
3 -> [0111 1011 1101 1110] .................................(lista mérete: 4C3 = 4)
4 -> [1111] ................................(lista-méret: 4C4 = 1)
Itt megfigyeljük, hogy minden listának N select Key mérete van, amely N select N/2-nél lesz a maximális
Mivel mind a 2-t ismételjükNpermutációk és a második felének hozzáfűzése a térképről. A térképen a legnagyobb méretű lista az N/2 pozícióban található.
A legrosszabb eset N/2 pozícióban fordul elő, ahol az NCN/2 = N!/(N/2)-t kell bejárnunk!2permutációk.
sql sorrendben véletlenszerűen
Időbonyolultság: O(2N* N!/(N/2)!2)
Segédtér: O(2N) mert minden N méretű bináris karakterlánc-permutációt tárolunk
