Egy tömb fix méretű, homogén adatszerkezet . A tömbök korlátozása az, hogy méretük rögzített. Ez azt jelenti, hogy a tömb deklarálása során meg kell adnunk az elemek számát. Itt felmerül a kérdés, hogy mi van akkor, ha egy elemet akarunk beszúrni, és nem marad több hely az új elemnek? Itt a fogalma dinamikus tömb létrejön. Dinamikusan kiadja a tömb méretét.
Ebben a részben meg fogjuk érteni mi az a dinamikus tömb, a dinamikus tömb jellemzői, a dinamikus tömb átméretezése, és hogyan valósítsuk meg a dinamikus tömböt Java-ban .
Mi az a dinamikus tömb?
A dinamikus tömb a változó méretű lista adatszerkezet. Automatikusan növekszik, amikor megpróbálunk beszúrni egy elemet, ha nem marad több hely az új elem számára. Lehetővé teszi elemek hozzáadását és eltávolítását. Futás közben lefoglalja a memóriát a kupac segítségével. Működés közben változtathatja a méretét.
Ban ben Jáva , Tömb lista egy átméretezhető megvalósítás. Megvalósítja a Lista felületet, és biztosítja a lista műveletekhez kapcsolódó összes metódust. A dinamikus tömb erőssége:
dijkstra
- Gyors keresés
- Változó méret
- Gyorsítótár-barát
A dinamikus tömb működése
A dinamikus tömbben az elemek egymás mellett tárolódnak a tömb kezdetétől, és a fennmaradó hely kihasználatlanul marad. Addig adhatjuk az elemeket, amíg a lefoglalt térközt teljesen el nem fogy. Amikor a lefoglalt terület elfogy, és néhány elem hozzáadása szükséges. Ilyen esetben a fix méretű tömb méretét növelni kell. Vegye figyelembe, hogy az elem hozzáfűzése előtt lefoglalunk egy nagyobb tömböt, kimásoljuk az elemeket a tömbből, és visszaadjuk az újonnan létrehozott tömböt.
Egy másik lehetőség az elemek hozzáadására, hogy először hozzon létre egy függvényt, amely létrehoz egy új, dupla méretű tömböt, kimásolja az összes elemet a régi tömbből, és visszaadja az új tömböt. Hasonlóképpen csökkenthetjük a dinamikus tömb méretét is.
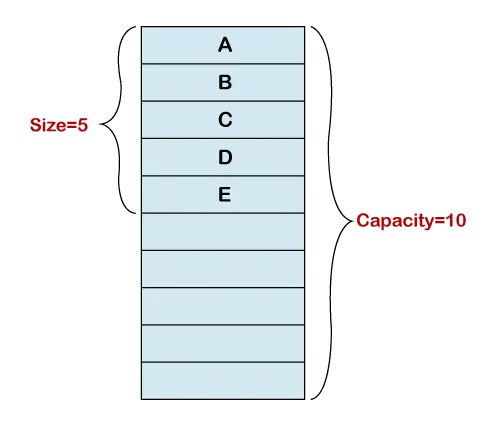
Méret vs. kapacitás
Egy dinamikus tömb inicializálása fix méretű tömböt hoz létre. A következő ábrán a tömb megvalósításának 10 indexe van. Öt elemet adtunk a tömbhöz. Most az alapul szolgáló tömb hossza öt. Ezért a dinamikus tömb mérete hossza 5, kapacitása pedig 10. A dinamikus tömb nyomon követi a végpontot.
nyomtatási csillag minta
A Dynamic Array jellemzői
A Java nyelven a dinamikus tömb három fő funkcióval rendelkezik: Elem hozzáadása, elem törlése és egy tömb átméretezése.
Elem hozzáadása dinamikus tömbhöz
A dinamikus tömbben létrehozhatunk egy rögzített méretű tömböt, ha további elemeket kell hozzáadnunk a tömbhöz. Általában egy új, dupla méretű tömböt hoz létre. Ezt követően az összes elemet átmásolja az újonnan létrehozott tömbbe. A következő megközelítést alkalmazzuk:

Elem törlése a dinamikus tömbből
Ha egy elemet szeretnénk eltávolítani a tömbből a megadott indexen, akkor a RemoveAt(i) módszer. A metódus elemzi a törölni kívánt elem indexszámát. Az elem törlése után a fennmaradó elemeket (a törölt elemhez jobbra eső elemeket) balra tolja a megadott indexszámtól. Használjuk a remove() metódust is, amely egy elemet töröl a tömb végéről. Az elemek eltolása után tárolja 0 az utolsó elem palotájában. Értsük meg egy példán keresztül, amint azt az alábbi ábrán is bemutattuk.

Dinamikus tömb átméretezése Java nyelven
Egy tömböt két esetben kell átméreteznünk, ha:
- A tömb a szükségesnél több memóriát használ.
- A tömb az összes memóriát elfoglalja, és elemeket kell hozzáadnunk.
Az első esetben a srinkSize() módszer átméretezni a sor . Csökkenti a tömb méretét. Felszabadítja a felesleges vagy fel nem használt memóriát. A második esetben a növekszik() módszer a tömb átméretezésére. Növeli a tömb méretét.
Ez költséges művelet, mert nagyobb tömböt igényel, és az összes elemet az előző tömbből másolja, majd visszaadja az új tömböt.

Tegyük fel, hogy a fenti tömbben további hat elemet kell hozzáadni, és a tömbben nem marad több memória az elemek tárolására. Ilyen esetekben a tömböt a növekszik() módszer.

Dinamikus tömb inicializálása
A dinamikus tömb inicializálása megegyezik a statikus tömb inicializálásával. Tekintsük a következő Java programot, amely egy dinamikus tömböt inicializál.
InitializeDynamicArray.java
public class InitializeDynamicArray { public static void main(String[] args) { //declaring array int array[]; //initialize an array array= new int[6]; //adding elements to the array array[0] = 34; array[1] = 90; array[2] = 12; array[3] = 22; array[4] = 9; array[5] = 27; System.out.print('Elements of Array are: '); //iteraton over the array for(int i=0; i <array.length ; i++) { system.out.print(array[i] +' '); } < pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <pre> Elements of Array are: 34 90 12 22 9 27 </pre> <p>Let's implement the operations in a Java program that we have discussed above.</p> <p> <strong>DynamicArrayExample1.java</strong> </p> <pre> public class DynamicArrayExample1 { private int array[]; private int count; private int sizeofarray; //creating a constructor of the class that initializes the values public DynamicArrayExample1() { array = new int[1]; count = 0; sizeofarray = 1; } //creating a function that appends an element at the end of the array public void addElement(int a) { //compares if the number of elements is equal to the size of the array or not if (count == sizeofarray) { //invoking the growSize() method that creates an array of double size growSize(); } //appens an element at the end of the array array[count] = a; count++; } //function that creates an array of double size public void growSize() { //declares a temp[] array int temp[] = null; if (count == sizeofarray) { //initialize a double size array of array temp = new int[sizeofarray * 2]; { for (int i = 0; i <sizeofarray; i++) { copies all the elements of old array temp[i]="array[i];" } sizeofarray="sizeofarray" * 2; creating a function that deletes an element at specified index public void addelementat(int index, int a) compare size with number if not equal grows (count="=" sizeofarray) invoking growsize() method growsize(); for (int i="count" - 1;>= index; i--) { //shifting all the elements to the left from the specified index array[i + 1] = array[i]; } //inserts an element at the specified index array[index] = a; count++; } public static void main(String[] args) { DynamicArrayExample1 da = new DynamicArrayExample1(); //adding elements to the array da.addElement(12); da.addElement(22); da.addElement(35); da.addElement(47); da.addElement(85); da.addElement(26); da.addElement(70); da.addElement(81); da.addElement(96); da.addElement(54); System.out.println('Elements of the array:'); //iterate over the array for accessing the elements for (int i = 0; i <da.sizeofarray; 5 99 i++) { system.out.print(da.array[i] + ' '); } system.out.println(); determines and prints the size number of elements array system.out.println('size array: da.sizeofarray); system.out.println('no. in da.count); invoking method to add an element at specified index da.addelementat(5, 99); where is be system.out.println('
elements after adding 5:'); iterate over for accessing (int i="0;" < da.sizeofarray; pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/java-tutorial/02/dynamic-array-java-6.webp" alt="Dynamic Array in Java"> <p>Let's shrink the array, delete the last element, and a specified element from the array.</p> <p> <strong>DynamicArrayExample2.java</strong> </p> <pre> public class DynamicArrayExample2 { private int array[]; private int count; private int sizeofarray; //creating a constructor of the class that initializes the values public DynamicArrayExample2() { array = new int[1]; count = 0; sizeofarray = 1; } //creating a function that appends an element at the end of the array public void addElement(int a) { //compares if the number of elements is equal to the size of the array or not if (count == sizeofarray) { //invoking the growSize() method that creates an array of double size growSize(); } //appens an element at the end of the array array[count] = a; count++; } //function that creates an array of double size public void growSize() { //declares a temp[] array int temp[] = null; if (count == sizeofarray) { //initialize a double size array of array temp = new int[sizeofarray * 2]; { for (int i = 0; i <sizeofarray; i++) { copies all the elements of old array temp[i]="array[i];" } sizeofarray="sizeofarray" * 2; method removes unused space public void shrinksize() declares a temp[] int if (count> 0) { //creates an array of the size equal to the count i.e. number of elements the array have temp = new int[count]; for (int i = 0; i <count; i++) { copies all the elements of old array temp[i]="array[i];" } sizeofarray="count;" creating a function that removes last for public void removeelement() if (count> 0) { array[count - 1] = 0; count--; } } //creating a function that delets an element from the specified index public void removeElementAt(int index) { if (count > 0) { for (int i = index; i <count 7 - 1; i++) { shifting all the elements to left from specified index array[i]="array[i" + 1]; } array[count 1]="0;" count--; public static void main(string[] args) dynamicarrayexample2 da="new" dynamicarrayexample2(); adding array da.addelement(12); da.addelement(22); da.addelement(35); da.addelement(47); da.addelement(85); da.addelement(26); da.addelement(70); da.addelement(81); da.addelement(96); da.addelement(54); system.out.println('elements of array:'); iterate over for accessing (int i="0;" < da.sizeofarray; system.out.print(da.array[i] ' '); system.out.println(); determines and prints size number system.out.println('size array: da.sizeofarray); system.out.println('no. in da.count); invoking method delete last element da.removeelement(); after deleting system.out.print('
elements element: system.out.print('no. da.count+'
'); that deletes an da.removeelementat(7); at 7: pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/java-tutorial/02/dynamic-array-java-7.webp" alt="Dynamic Array in Java"> <hr></count></count;></sizeofarray;></pre></da.sizeofarray;></sizeofarray;></pre></array.length> Valósítsuk meg a fentebb tárgyalt műveleteket egy Java programban.
karakterlánc
DynamicArrayExample1.java
public class DynamicArrayExample1 { private int array[]; private int count; private int sizeofarray; //creating a constructor of the class that initializes the values public DynamicArrayExample1() { array = new int[1]; count = 0; sizeofarray = 1; } //creating a function that appends an element at the end of the array public void addElement(int a) { //compares if the number of elements is equal to the size of the array or not if (count == sizeofarray) { //invoking the growSize() method that creates an array of double size growSize(); } //appens an element at the end of the array array[count] = a; count++; } //function that creates an array of double size public void growSize() { //declares a temp[] array int temp[] = null; if (count == sizeofarray) { //initialize a double size array of array temp = new int[sizeofarray * 2]; { for (int i = 0; i <sizeofarray; i++) { copies all the elements of old array temp[i]="array[i];" } sizeofarray="sizeofarray" * 2; creating a function that deletes an element at specified index public void addelementat(int index, int a) compare size with number if not equal grows (count="=" sizeofarray) invoking growsize() method growsize(); for (int i="count" - 1;>= index; i--) { //shifting all the elements to the left from the specified index array[i + 1] = array[i]; } //inserts an element at the specified index array[index] = a; count++; } public static void main(String[] args) { DynamicArrayExample1 da = new DynamicArrayExample1(); //adding elements to the array da.addElement(12); da.addElement(22); da.addElement(35); da.addElement(47); da.addElement(85); da.addElement(26); da.addElement(70); da.addElement(81); da.addElement(96); da.addElement(54); System.out.println('Elements of the array:'); //iterate over the array for accessing the elements for (int i = 0; i <da.sizeofarray; 5 99 i++) { system.out.print(da.array[i] + \' \'); } system.out.println(); determines and prints the size number of elements array system.out.println(\'size array: da.sizeofarray); system.out.println(\'no. in da.count); invoking method to add an element at specified index da.addelementat(5, 99); where is be system.out.println(\'
elements after adding 5:\'); iterate over for accessing (int i="0;" < da.sizeofarray; pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/java-tutorial/02/dynamic-array-java-6.webp" alt="Dynamic Array in Java"> <p>Let's shrink the array, delete the last element, and a specified element from the array.</p> <p> <strong>DynamicArrayExample2.java</strong> </p> <pre> public class DynamicArrayExample2 { private int array[]; private int count; private int sizeofarray; //creating a constructor of the class that initializes the values public DynamicArrayExample2() { array = new int[1]; count = 0; sizeofarray = 1; } //creating a function that appends an element at the end of the array public void addElement(int a) { //compares if the number of elements is equal to the size of the array or not if (count == sizeofarray) { //invoking the growSize() method that creates an array of double size growSize(); } //appens an element at the end of the array array[count] = a; count++; } //function that creates an array of double size public void growSize() { //declares a temp[] array int temp[] = null; if (count == sizeofarray) { //initialize a double size array of array temp = new int[sizeofarray * 2]; { for (int i = 0; i <sizeofarray; i++) { copies all the elements of old array temp[i]="array[i];" } sizeofarray="sizeofarray" * 2; method removes unused space public void shrinksize() declares a temp[] int if (count> 0) { //creates an array of the size equal to the count i.e. number of elements the array have temp = new int[count]; for (int i = 0; i <count; i++) { copies all the elements of old array temp[i]="array[i];" } sizeofarray="count;" creating a function that removes last for public void removeelement() if (count> 0) { array[count - 1] = 0; count--; } } //creating a function that delets an element from the specified index public void removeElementAt(int index) { if (count > 0) { for (int i = index; i <count 7 - 1; i++) { shifting all the elements to left from specified index array[i]="array[i" + 1]; } array[count 1]="0;" count--; public static void main(string[] args) dynamicarrayexample2 da="new" dynamicarrayexample2(); adding array da.addelement(12); da.addelement(22); da.addelement(35); da.addelement(47); da.addelement(85); da.addelement(26); da.addelement(70); da.addelement(81); da.addelement(96); da.addelement(54); system.out.println(\'elements of array:\'); iterate over for accessing (int i="0;" < da.sizeofarray; system.out.print(da.array[i] \' \'); system.out.println(); determines and prints size number system.out.println(\'size array: da.sizeofarray); system.out.println(\'no. in da.count); invoking method delete last element da.removeelement(); after deleting system.out.print(\'
elements element: system.out.print(\'no. da.count+\'
\'); that deletes an da.removeelementat(7); at 7: pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/java-tutorial/02/dynamic-array-java-7.webp" alt="Dynamic Array in Java"> <hr></count></count;></sizeofarray;></pre></da.sizeofarray;></sizeofarray;>