Adva egy egyedülálló összekapcsolt listát, a feladat a lista középső csomópontjának törlése.
- Ha a lista egyenletes számú csomópontot tartalmaz, akkor két középső csomópont lesz. Ebben az esetben törölje a második középső csomópontot.
- Ha a kapcsolódó lista csak egy csomópontból áll, akkor a NULL visszatérése.
Példa:
olyan webhelyek, mint a bedpage
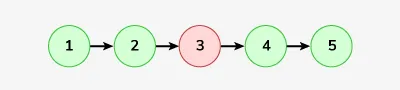
Bemenet: LinkedList: 1-> 2-> 3-> 4-> 5
Kimenet: 1-> 2-> 4-> 5
Magyarázat:
Bemenet: LinkedList: 2-> 4-> 6-> 7-> 5-> 1
Kimenet: 2-> 4-> 6-> 5-> 1
Magyarázat: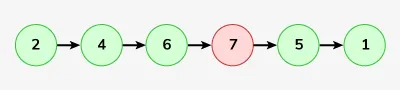
Bemenet: LinkedList: 7
Kimenet:python új vonal
Tartalomjegyzék
- [Naiv megközelítés] Két átjáró - O (N) idő és o (1) tér felhasználásával
- [Várható megközelítés] Egypasszális áthaladás lassú és gyors mutatókkal - o (n) idő és o (1) tér
[Naiv megközelítés] Két átjáró - O (N) idő és o (1) tér felhasználásával
Ennek a megközelítésnek az alapvető ötlete az, hogy először átlépjük a teljes linkelt listát, hogy megszámolják a csomópontok számát. Miután megtudtuk a csomópontok teljes számát, kiszámíthatjuk a középső csomópont helyzetét, amely az indexnél van n/2 (ahol n a csomópontok teljes száma). Ezután menjen újra a kapcsolódó listán, de ezúttal közvetlenül a középső csomópont előtt állunk meg. Miután odamentünk, módosítjuk a csomópont következő mutatóját a középső csomópont előtt, hogy átugorjon a középső csomóponton, és közvetlenül az utána mutató csomópontra mutat
Az alábbiakban a fenti megközelítés megvalósítása:
C++// C++ program to delete middle of a linked list #include
// C program to delete middle of a linked list #include
// Java program to delete middle of a linked list class Node { int data; Node next; Node(int x) { data = x; next = null; } } public class GfG { // Function to delete middle node from linked list. public static Node deleteMid(Node head) { // Edge case: return null if there is only // one node. if (head.next == null) return null; int count = 0; Node p1 = head p2 = head; // First pass count the number of nodes // in the linked list using 'p1'. while (p1 != null) { count++; p1 = p1.next; } // Get the index of the node to be deleted. int middleIndex = count / 2; // Second pass let 'p2' move toward predecessor // of the middle node. for (int i = 0; i < middleIndex - 1; ++i) p2 = p2.next; // Delete the middle node and return 'head'. p2.next = p2.next.next; return head; } public static void printList(Node head) { Node temp = head; while (temp != null) { System.out.print(temp.data + ' -> '); temp = temp.next; } System.out.println('null'); } public static void main(String[] args) { // Create a static hardcoded linked list: // 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5. Node head = new Node(1); head.next = new Node(2); head.next.next = new Node(3); head.next.next.next = new Node(4); head.next.next.next.next = new Node(5); System.out.print('Original Linked List: '); printList(head); // Delete the middle node. head = deleteMid(head); System.out.print ('Linked List after deleting the middle node: '); printList(head); } }
# Python3 program to delete middle of a linked list class Node: def __init__(self data): self.data = data self.next = None # Function to delete middle node from linked list. def deleteMid(head): # Edge case: return None if there is only # one node. if head.next is None: return None count = 0 p1 = head p2 = head # First pass count the number of nodes # in the linked list using 'p1'. while p1 is not None: count += 1 p1 = p1.next # Get the index of the node to be deleted. middleIndex = count // 2 # Second pass let 'p2' move toward the predecessor # of the middle node. for i in range(middleIndex - 1): p2 = p2.next # Delete the middle node and return 'head'. p2.next = p2.next.next return head def printList(head): temp = head while temp is not None: print(temp.data end=' -> ') temp = temp.next print('None') if __name__ == '__main__': # Create a static hardcoded linked list: # 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5. head = Node(1) head.next = Node(2) head.next.next = Node(3) head.next.next.next = Node(4) head.next.next.next.next = Node(5) print('Original Linked List:' end=' ') printList(head) # Delete the middle node. head = deleteMid(head) print('Linked List after deleting the middle node:' end=' ') printList(head)
// C# program to delete middle of a linked list using System; class Node { public int data; public Node next; public Node(int x) { data = x; next = null; } } class GfG { // Function to delete middle node from linked list. static Node deleteMid(Node head) { // Edge case: return null if there is only // one node. if (head.next == null) return null; int count = 0; Node p1 = head p2 = head; // First pass count the number of nodes // in the linked list using 'p1'. while (p1 != null) { count++; p1 = p1.next; } // Get the index of the node to be deleted. int middleIndex = count / 2; // Second pass let 'p2' move toward the predecessor // of the middle node. for (int i = 0; i < middleIndex - 1; ++i) p2 = p2.next; // Delete the middle node and return 'head'. p2.next = p2.next.next; return head; } static void printList(Node head) { Node temp = head; while (temp != null) { Console.Write(temp.data + ' -> '); temp = temp.next; } Console.WriteLine('null'); } static void Main(string[] args) { // Create a static hardcoded linked list: // 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5. Node head = new Node(1); head.next = new Node(2); head.next.next = new Node(3); head.next.next.next = new Node(4); head.next.next.next.next = new Node(5); Console.Write('Original Linked List: '); printList(head); // Delete the middle node. head = deleteMid(head); Console.Write ('Linked List after deleting the middle node: '); printList(head); } }
class Node { constructor(data) { this.data = data; this.next = null; } } // Function to delete middle node from linked list. function deleteMid(head) { // Edge case: return null if there is only // one node. if (head.next === null) return null; let count = 0; let p1 = head p2 = head; // First pass count the number of nodes // in the linked list using 'p1'. while (p1 !== null) { count++; p1 = p1.next; } // Get the index of the node to be deleted. let middleIndex = Math.floor(count / 2); // Second pass let 'p2' move toward the predecessor // of the middle node. for (let i = 0; i < middleIndex - 1; ++i) p2 = p2.next; // Delete the middle node and return 'head'. p2.next = p2.next.next; return head; } function printList(head) { let temp = head; while (temp !== null) { console.log(temp.data + ' -> '); temp = temp.next; } console.log('null'); } // Create a static hardcoded linked list: // 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5. let head = new Node(1); head.next = new Node(2); head.next.next = new Node(3); head.next.next.next = new Node(4); head.next.next.next.next = new Node(5); console.log('Original Linked List: '); printList(head); // Delete the middle node. head = deleteMid(head); console.log('Linked List after deleting the middle node: '); printList(head);
Kibocsátás
Original Linked List: 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5 -> nullptr Linked List after deleting the middle node: 1 -> 2 -> 4 -> 5 -> nullptr
Idő bonyolultsága: On). A kapcsolt lista két átjárására van szükség
Kiegészítő hely: O (1). Nincs szükség extra helyre.
[Várható megközelítés] Egypasszális áthaladás lassú és gyors mutatókkal - o (n) idő és o (1) tér
A fenti megoldás megköveteli a kapcsolódó lista két átjárását. A középső csomópont egy átjárással törölhető. Az ötlet az, hogy két mutatót használjon lassú_ptr és FAST_PTR - A gyors mutató egyszerre két csomópontot mozgat, míg a lassú mutató egyszerre egy csomópontot mozgat. Amikor a gyors mutató eléri a lista végét, a lassú mutató a középső csomóponton helyezkedik el. Ezután csatlakoznia kell a középső csomópont előtti csomóponthoz ( előző ) a középső csomópont után érkező csomóponthoz. Ez ténylegesen átugorja a középső csomópontot, eltávolítva azt a listáról.
beállítva java-ban
Az alábbiakban bemutatjuk a fenti megközelítés végrehajtását
C++// C++ program to delete middle of a linked list #include
// C program to delete middle of a linked list #include
// Java program to delete the middle of a linked list class Node { int data; Node next; Node(int x) { data = x; next = null; } } class GfG { // Function to delete middle node from linked list static Node deleteMid(Node head) { // If the list is empty return null if (head == null) return null; // If the list has only one node // delete it and return null if (head.next == null) { return null; } Node prev = null; Node slow_ptr = head; Node fast_ptr = head; // Move the fast pointer 2 nodes ahead // and the slow pointer 1 node ahead // until fast pointer reaches end of list while (fast_ptr != null && fast_ptr.next != null) { fast_ptr = fast_ptr.next.next; // Update prev to hold the previous // slow pointer value prev = slow_ptr; slow_ptr = slow_ptr.next; } // At this pointslow_ptr points to middle node // Bypass the middle node prev.next = slow_ptr.next; // Return the head of the modified list return head; } static void printList(Node head) { Node temp = head; while (temp != null) { System.out.print(temp.data + ' -> '); temp = temp.next; } System.out.println('NULL'); } public static void main(String[] args) { // Create a static hardcoded linked list: // 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5 Node head = new Node(1); head.next = new Node(2); head.next.next = new Node(3); head.next.next.next = new Node(4); head.next.next.next.next = new Node(5); System.out.print('Original Linked List: '); printList(head); // Delete the middle node head = deleteMid(head); System.out.print ('Linked List after deleting the middle node: '); printList(head); } }
# Python program to delete the middle of a linked list class Node: def __init__(self data): self.data = data self.next = None # Function to delete middle node from linked list def deleteMid(head): # If the list is empty return None if head is None: return None # If the list has only one node # delete it and return None if head.next is None: return None prev = None slow_ptr = head fast_ptr = head # Move the fast pointer 2 nodes ahead # and the slow pointer 1 node ahead # until fast pointer reaches end of the list while fast_ptr is not None and fast_ptr.next is not None: fast_ptr = fast_ptr.next.next # Update prev to hold the previous # slow pointer value prev = slow_ptr slow_ptr = slow_ptr.next # At this point slow_ptr points to middle node # Bypass the middle node prev.next = slow_ptr.next # Return the head of the modified list return head def printList(head): temp = head while temp: print(temp.data end=' -> ') temp = temp.next print('NULL') if __name__ == '__main__': # Create a static hardcoded linked list: # 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5 head = Node(1) head.next = Node(2) head.next.next = Node(3) head.next.next.next = Node(4) head.next.next.next.next = Node(5) print('Original Linked List: ' end='') printList(head) # Delete the middle node head = deleteMid(head) print('Linked List after deleting the middle node: ' end='') printList(head)
// C# program to delete middle of a linked list using System; class Node { public int data; public Node next; public Node(int x) { data = x; next = null; } } class GfG { // Function to delete middle node from linked list public static Node deleteMid(Node head) { // If the list is empty return null if (head == null) return null; // If the list has only one node // delete it and return null if (head.next == null) { return null; } Node prev = null; Node slow_ptr = head; Node fast_ptr = head; // Move the fast pointer 2 nodes ahead // and the slow pointer 1 node ahead // until fast pointer reaches end of the list while (fast_ptr != null && fast_ptr.next != null) { fast_ptr = fast_ptr.next.next; // Update prev to hold the previous // slow pointer value prev = slow_ptr; slow_ptr = slow_ptr.next; } // At this point slow_ptr points to middle node // Bypass the middle node prev.next = slow_ptr.next; // Return the head of the modified list return head; } // Function to print the linked list public static void printList(Node head) { Node temp = head; while (temp != null) { Console.Write(temp.data + ' -> '); temp = temp.next; } Console.WriteLine('NULL'); } public static void Main(string[] args) { // Create a static hardcoded linked list: // 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5 Node head = new Node(1); head.next = new Node(2); head.next.next = new Node(3); head.next.next.next = new Node(4); head.next.next.next.next = new Node(5); Console.Write('Original Linked List: '); printList(head); // Delete the middle node head = deleteMid(head); Console.Write ('Linked List after deleting the middle node: '); printList(head); } }
// javascript program to delete middle of a linked list class Node { constructor(data) { this.data = data; this.next = null; } } // Function to delete the middle node from the linked list function deleteMid(head) { // If the list is empty return null if (head === null) { return null; } // If the list has only one node delete it and return // null if (head.next === null) { return null; } let prev = null; let slow_ptr = head; let fast_ptr = head; // Move the fast pointer 2 nodes ahead // and the slow pointer 1 node ahead // until the fast pointer reaches the end of the list while (fast_ptr !== null && fast_ptr.next !== null) { fast_ptr = fast_ptr.next.next; // Update prev to hold the previous slow pointer // value prev = slow_ptr; slow_ptr = slow_ptr.next; } // At this point slow_ptr points to the middle node // Bypass the middle node prev.next = slow_ptr.next; // Return the head of the modified list return head; } function printList(head) { let temp = head; while (temp !== null) { process.stdout.write(temp.data + ' -> '); temp = temp.next; } console.log('null'); } // Create a static hardcoded linked list: // 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5 let head = new Node(1); head.next = new Node(2); head.next.next = new Node(3); head.next.next.next = new Node(4); head.next.next.next.next = new Node(5); process.stdout.write('Original Linked List: '); printList(head); // Delete the middle node head = deleteMid(head); process.stdout.write( 'Linked List after deleting the middle node: '); printList(head);
Kibocsátás
Original Linked List: 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5 -> NULL Linked List after deleting the middle node: 1 -> 2 -> 4 -> 5 -> NULL
Idő bonyolultsága: On). Csak a kapcsolt lista áthaladására van szükség
Kiegészítő hely: O (1). Mivel nincs szükség extra helyre.
Kapcsolódó cikk:
- Keresse meg a linkelt lista közepét


