A C++ nyelvben az öröklődés egy olyan folyamat, amelyben egy objektum automatikusan megszerzi a szülőobjektuma összes tulajdonságát és viselkedését. Ilyen módon újra felhasználhatja, kiterjesztheti vagy módosíthatja a más osztályokban meghatározott attribútumokat és viselkedéseket.
A C++-ban azt az osztályt, amely egy másik osztály tagjait örökli, származtatott osztálynak, azt az osztályt pedig, amelynek tagjai öröklődnek, alaposztálynak nevezzük. A származtatott osztály az alaposztály speciális osztálya.
A C++ öröklődés előnyei
A kód újrafelhasználhatósága: Most újra felhasználhatja a szülőosztály tagjait. Tehát nem szükséges újra meghatározni a tagot. Így kevesebb kódra van szükség az osztályban.
elsődleges kulcs és összetett kulcs SQL-ben
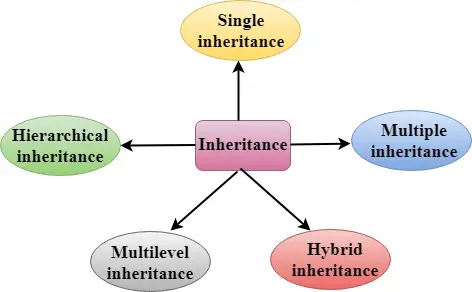
Az öröklődés típusai
A C++ ötféle öröklődést támogat:
- Egyszeri öröklés
- Többszörös öröklés
- Hierarchikus öröklődés
- Többszintű öröklődés
- Hibrid öröklődés
Származtatott osztályok
A származtatott osztály az alaposztályból származó osztály.
java helyettesítés
A származtatott osztály szintaxisa:
|_+_|A fenti esetben a származtatott osztály függvénye felülírja az alaposztály metódusát. Ezért a display() függvény meghívása egyszerűen a származtatott osztályban definiált függvényt hívja meg. Ha meg akarjuk hívni az alaposztályfüggvényt, használhatjuk az osztályfeloldó operátort.
int main() { B b; b.display(); // Calling the display() function of B class. b.B :: display(); // Calling the display() function defined in B class. } C++ hibrid öröklődés
A hibrid öröklődés egynél több öröklődéstípus kombinációja.

Lássunk egy egyszerű példát:
#include using namespace std; class A { protected: int a; public: void get_a() { std::cout << 'Enter the value of 'a' : ' <>a; } }; class B : public A { protected: int b; public: void get_b() { std::cout << 'Enter the value of 'b' : ' <>b; } }; class C { protected: int c; public: void get_c() { std::cout << 'Enter the value of c is : ' <>c; } }; class D : public B, public C { protected: int d; public: void mul() { get_a(); get_b(); get_c(); std::cout << 'Multiplication of a,b,c is : ' < <a*b*c<< std::endl; } }; int main() { d d; d.mul(); return 0; < pre> <p>Output:</p> <pre> Enter the value of 'a' : 10 Enter the value of 'b' : 20 Enter the value of c is : 30 Multiplication of a,b,c is : 6000 </pre> <h2>C++ Hierarchical Inheritance</h2> <p>Hierarchical inheritance is defined as the process of deriving more than one class from a base class.</p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/c-tutorial/62/c-inheritance-7.webp" alt="C++ Inheritance"> <p> <strong>Syntax of Hierarchical inheritance:</strong> </p> <pre> class A { // body of the class A. } class B : public A { // body of class B. } class C : public A { // body of class C. } class D : public A { // body of class D. } </pre> <p>Let's see a simple example:</p> <pre> #include using namespace std; class Shape // Declaration of base class. { public: int a; int b; void get_data(int n,int m) { a= n; b = m; } }; class Rectangle : public Shape // inheriting Shape class { public: int rect_area() { int result = a*b; return result; } }; class Triangle : public Shape // inheriting Shape class { public: int triangle_area() { float result = 0.5*a*b; return result; } }; int main() { Rectangle r; Triangle t; int length,breadth,base,height; std::cout << 'Enter the length and breadth of a rectangle: ' <>length>>breadth; r.get_data(length,breadth); int m = r.rect_area(); std::cout << 'Area of the rectangle is : ' <<m<< std::endl; std::cout << \\'enter the base and height of triangle: \\' <>base>>height; t.get_data(base,height); float n = t.triangle_area(); std::cout <<\\'area of the triangle is : \\' << n<<std::endl; return 0; } < pre> <p>Output:</p> <pre> Enter the length and breadth of a rectangle: 23 20 Area of the rectangle is : 460 Enter the base and height of the triangle: 2 5 Area of the triangle is : 5 </pre></\\'area></m<<></pre></a*b*c<<> C++ hierarchikus öröklődés
A hierarchikus öröklődés az a folyamat, amelynek során egynél több osztályt származtatunk egy alaposztályból.

A hierarchikus öröklődés szintaxisa:
class A { // body of the class A. } class B : public A { // body of class B. } class C : public A { // body of class C. } class D : public A { // body of class D. } Lássunk egy egyszerű példát:
mvc tavaszi keretben
#include using namespace std; class Shape // Declaration of base class. { public: int a; int b; void get_data(int n,int m) { a= n; b = m; } }; class Rectangle : public Shape // inheriting Shape class { public: int rect_area() { int result = a*b; return result; } }; class Triangle : public Shape // inheriting Shape class { public: int triangle_area() { float result = 0.5*a*b; return result; } }; int main() { Rectangle r; Triangle t; int length,breadth,base,height; std::cout << 'Enter the length and breadth of a rectangle: ' <>length>>breadth; r.get_data(length,breadth); int m = r.rect_area(); std::cout << 'Area of the rectangle is : ' <<m<< std::endl; std::cout << \\'enter the base and height of triangle: \\' <>base>>height; t.get_data(base,height); float n = t.triangle_area(); std::cout <<\\'area of the triangle is : \\' << n<<std::endl; return 0; } < pre> <p>Output:</p> <pre> Enter the length and breadth of a rectangle: 23 20 Area of the rectangle is : 460 Enter the base and height of the triangle: 2 5 Area of the triangle is : 5 </pre></\\'area></m<<>